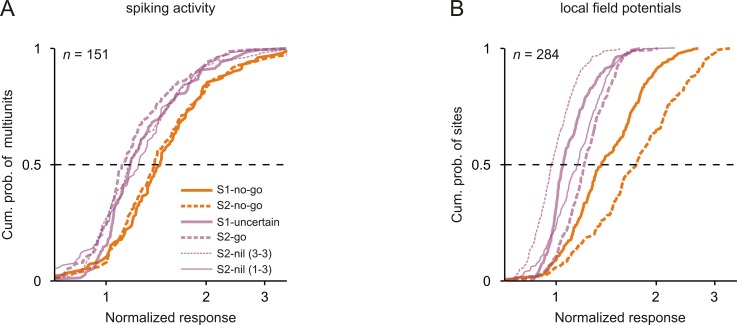
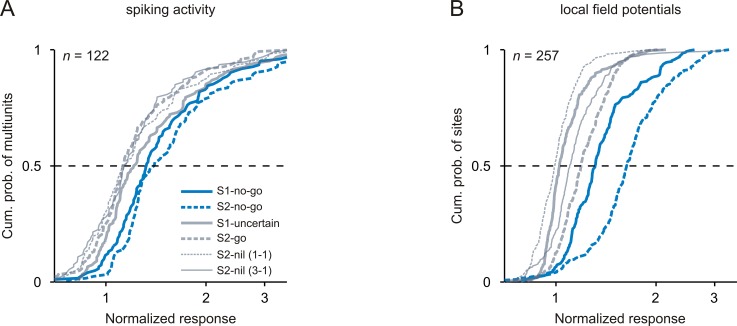
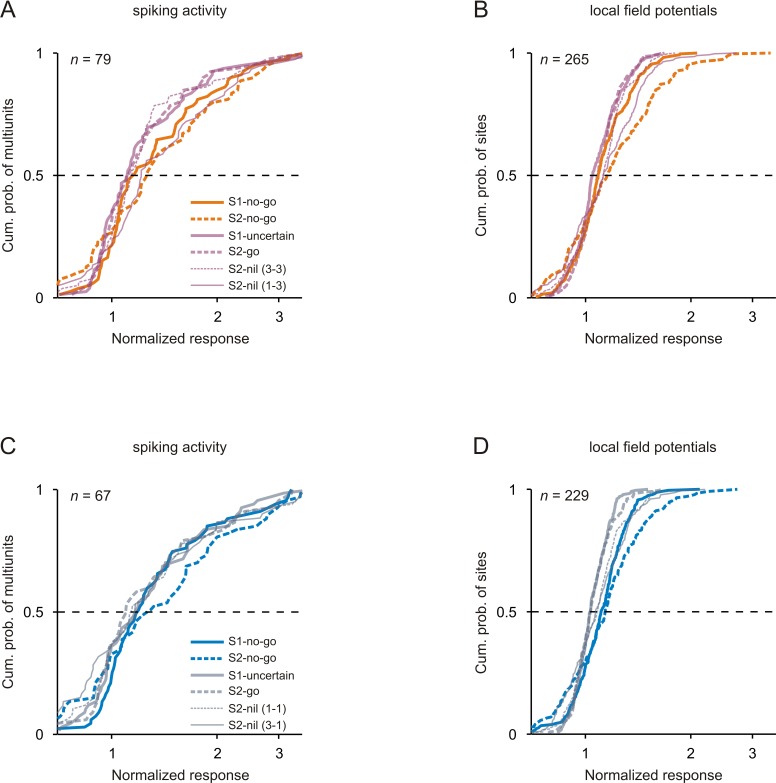
Figure 3. Neuronal responses were strongest to tones that signaled the no-go response.
Cumulative distributions of the normalized neuronal responses to the 3 kHz tone in the six conditions (different sensorimotor associations and positions) for spiking activity (A) and local field potentials (B). For each tone, the normalized neuronal response was calculated as the mean activity during the 250 ms period after tone onset, normalized to the mean activity during the 250 ms period directly before the tone.