Fig. 4.
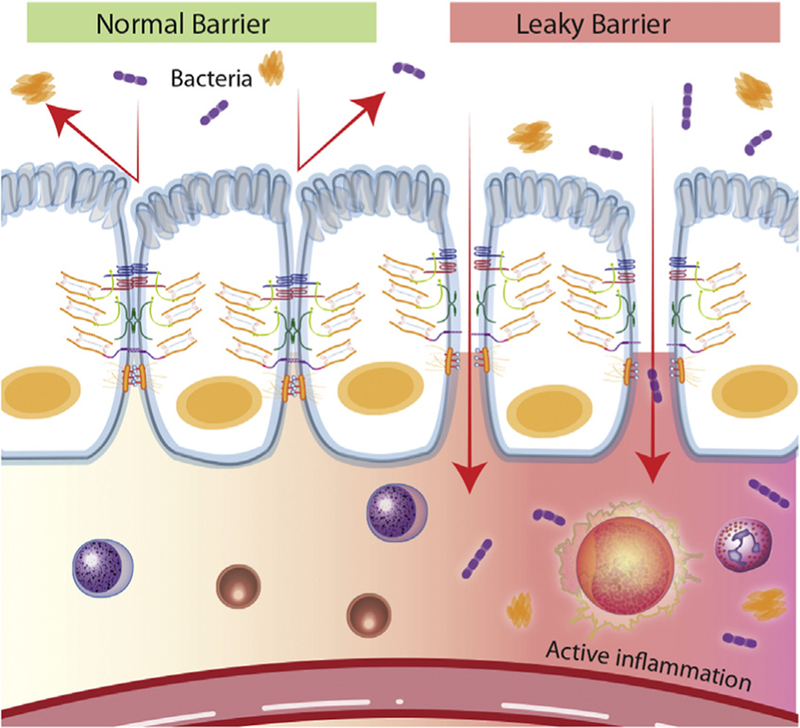
Normal versus impaired barrier function. The role of the intestinal epithelium is to provide a physical barrier against luminal contents such as bacteria. There are several important components of the barrier including tight junctions, adherens junctions, and desmosomes. Potentially harmful molecules cannot normally penetrate the barrier; however, when the barrier becomes compromised at any contact point, the passage of noxious molecules can occur and result in both an inflammatory and immune response. Disruption of the intestinal barrier may result in the development of local and systemic disease.
