Figure. HERV-K may initiate or propagate the inflammation that defines pulmonary arterial hypertension.
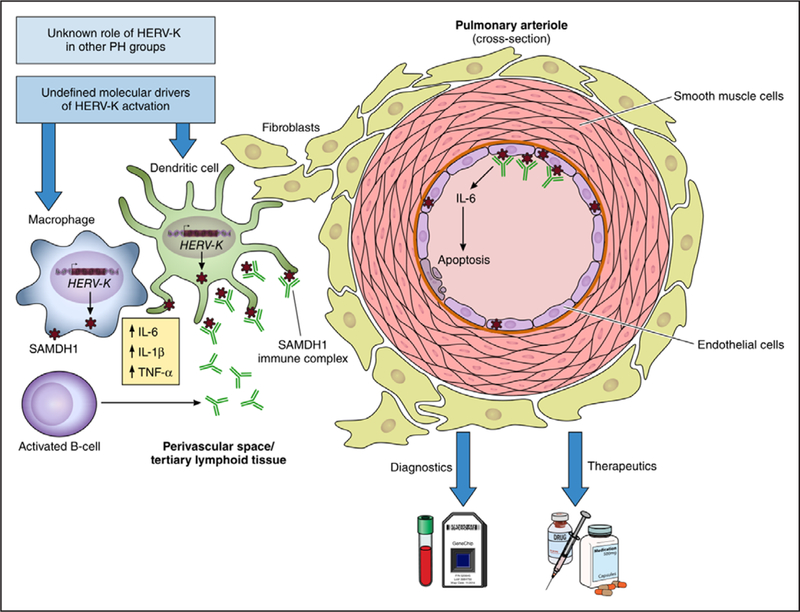
Saito and colleagues propose a role for HERV-K in the pathogenesis of PAH. Specifically, HERV-K components induce SAMDH1 expression, resulting in cytokine release, endothelial apoptosis, and B-cell activation. How HERV-K is activated or its diagnostic and therapeutic implications are still undefined. HERV-K indicates human endogenous retrovirus K; IL, interleukin; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; and TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
