Figure 1.
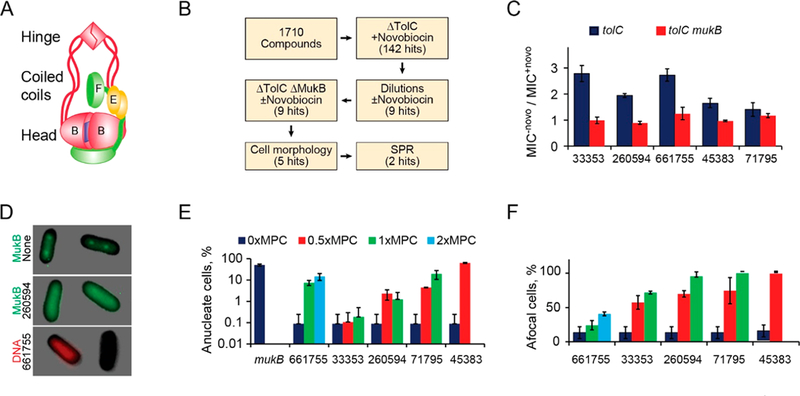
(A) Architecture of the E. coli condensin MukBEF. The SMC subunit MukB dimerizes via the hinge and the ATP (blue square) mediated interface at the head. MukEF dynamically interacts with the head. (B) Flowchart of the screen. (C) Ratios of minimal inhibitory concentrations of the five hits in the presence or absence of 0.25× MIC of novobiocin for ΔtolC and ΔtolCΔmukB cells (±SEM). (D) Examples of afocal and anucleate cells. MukB-GFP forms foci at 1/4 and 3/4 of the cell length in the absence (top) but not presence (middle) of a hit compound. Bottom panel shows Michellamine-induced formation of anucleate cells. (E, F) Frequency of anucleate (E) and afocal (F) cells at the indicated levels of the hit compounds, expressed as a fraction of the minimal potentiation concentration, MPC (n > 100; ±SD).
