Figure. Rates of Emergency Department (ED) Visits for Adverse Drug Events (ADEs) from the Most Commonly Implicated Oral Antibiotics, by Patient Age, Children ≤19 Years, United States, 2011-2015.
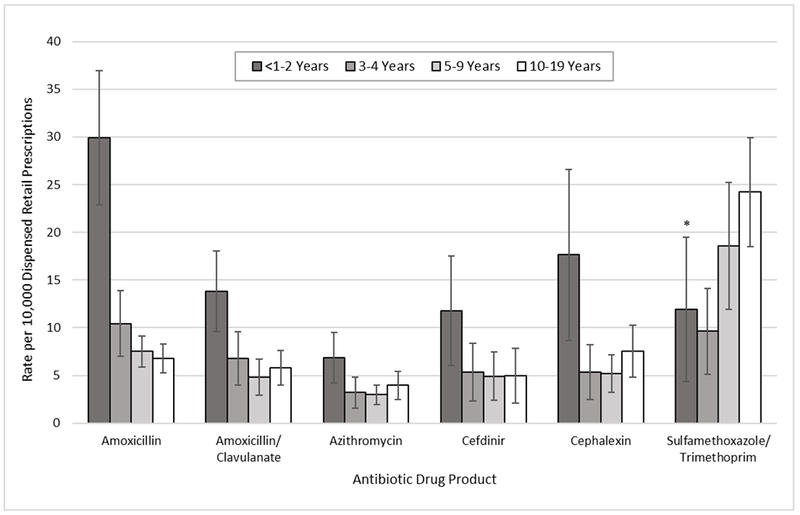
Estimates of ED visits for ADEs based on the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-Cooperative Adverse Drug Event Surveillance project (2011-2015); estimates of dispensed oral prescriptions from retail pharmacies based on the National Prescription Audit from QuintilesIMS (2011-2015). Drug products are not mutually exclusive; for some ED visits, more than one antibiotic was implicated in the ADE. Data exclude cases of unsupervised ingestion in which children aged ≤10 years accessed medications without caregiver oversight. *Coefficient of variation >30%.
