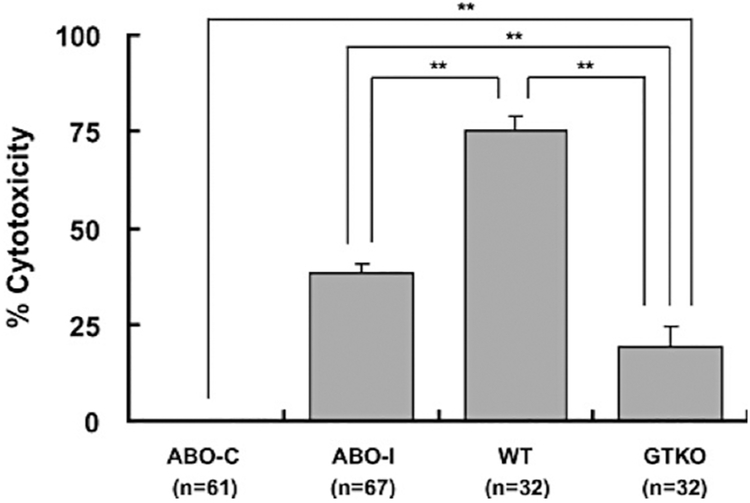
Figure 1: Human serum complement-dependent cytoxicity (CDC) of ABO-compatible human RBCs (ABO-C), ABO-incompatible human RBCs (ABO-I), wild-type pRBCs (WT), and GTKO pRBCs (GTKO).
Human sera (50%) of blood types O (n=10), A (n=9), B (n=8), and AB (n=4) were tested for CDC of human ABO-C, human ABO-I, pig WT, and pig GTKO RBCs. There was significantly greater lysis of WT than of ABO-I and GTKO RBCs (p<0.01). ABO-I RBCs sustained significantly greater lysis than of GTKO RBCs (p<0.01), but there was significantly greater lysis of GTKO than of ABO-C RBCs (**p<0.01). (Reproduced with permission from reference [52])