FIGURE 2.
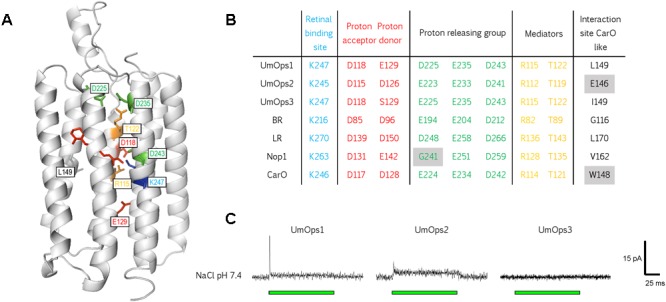
Structural conservation and physiological function of the three U. maydis rhodopsins. (A) Model of UmOps1 based on the crystal structure of the Acetabularia rhodopsin I with resolution of 1.57 Å (5awz.1) (Furuse et al., 2015). (B) Prominent residues that are well conserved in microbial rhodopsins of BR, LR, Nop1, CarO, and the three U. maydis rhodopsins. The respective position of the amino acids in the rhodopsin entity is given exemplary for UmOps1 in A. The well-conserved proton donor corresponding to Asp-96 in bacteriorhodopsin is replaced by a glutamate in UmOps1 and a serine in UmOps3. (C) Whole-cell patch-clamp analysis of the rhodopsins that were heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells. A 532 nm laser (green bar) was used for excitation. While UmOps1 and UmOps2 are green light-activated ion pumps, no light-dependent signal was observed for UmOps3.
