FIGURE 4.
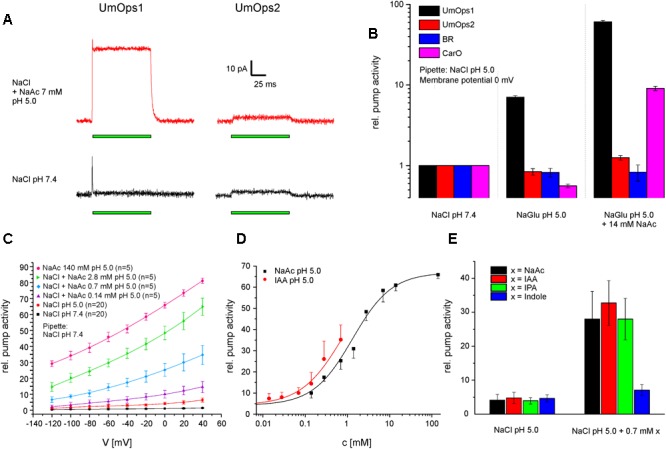
Effect of WOAs on the pump activity of U. maydis rhodopsins. (A) Typical whole cell traces showing the light-induced charge transfer by UmOps1 and UmOps2 (time of illumination is indicated by the green bar). The pump intensity of UmOps1 strongly increased in the presence of weak organic acids at external pH 5.0 (upper raw) compared to NaCl pH 7.4 (lower raw), while no such effect could be observed with UmOps2. (B) Mean relative pump activity and standard deviation of at least five experiments of UmOps1 and UmOps2 in comparison with BR and CarO (data were obtained from Adam et al., 2018) at 0 mV holding potential in NaCl pH 7.4, NaCl pH 5.0, and NaCl pH 5.0 supplemented with 14 mM sodium acetate. Note that only UmOps1 (similar to CarO) shows a clear response to acetate while UmOps2 does not. (C) Current–voltage relation of UmOps1 light-induced pump current in the presence of different concentrations of sodium acetate. (D) Dose-response of UmOps1 pump activity in sodium acetate and IAA. The sodium acetate data were described by a Hill function, revealing a k-value of 1.32 ± 0.18 mM. (E) Mean current and standard deviation of at least five experiments of UmOps1 pump activity in NaCl pH 5.0 and after adding 0.7 mM of different WOAs as indicated. Only the compounds with an acetate group showed a strong supporting effect on the pump activity.
