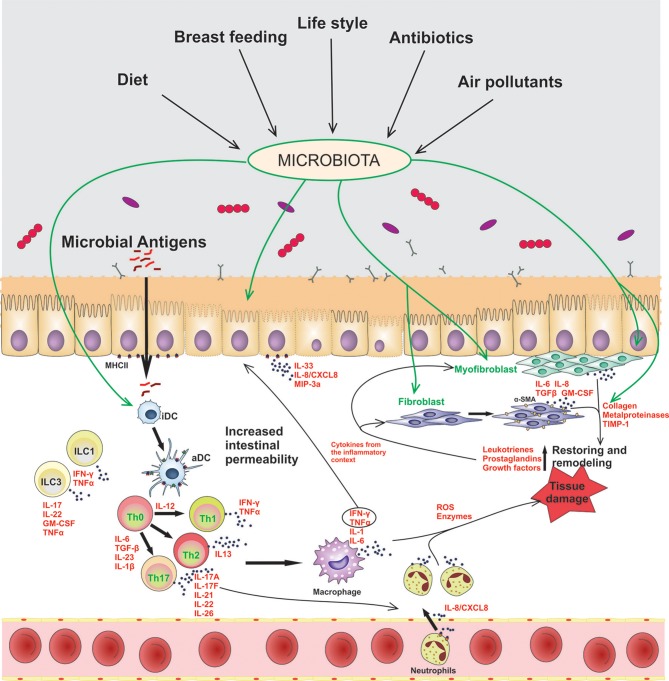
Figure 1.
Contribution of epithelial cells and intestinal fibroblasts to the induction and modulation of mucosal inflammation in IBD. In this disorder the intestinal barrier permeability is impaired, allowing the passage of luminal antigens into the lamina propria. The exposure of stromal and immune cells to the luminal content induces cell activation, inflammatory soluble-mediators release (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17A), cell-crosstalk (represented with arrows) and neutrophil recruitment to the inflamed tissue. Several environmental factors can modulate the microbiota composition and the activation of stromal and immune cells in the gut. iDC, innactivated dendritic cells; aDC, activated dendritic cells; ILCs, innate lymphoid cells; Th, T helper cells.