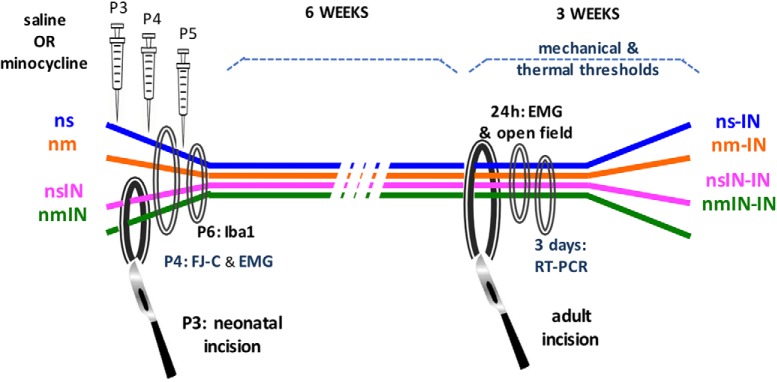
Figure 1.
Schematic of experimental design. Treatment groups included the following: ns, nm, nsIN, and nmIN. Injections were performed on P3, P4, and P5. All animals the underwent incision in adulthood (ns-IN, nm-IN, nsIN-IN, nmIN-IN). Evaluations included the following: measures of reflex sensitivity with mechanical withdrawal threshold, thermal withdrawal latency and EMG recordings; spontaneous activity in open field; neonatal spinal tissue analysis with FJ-C staining and Iba1 immunohistochemistry; and spinal gene expression with qRT-PCR following adult incision. In additional experiments, treatment groups included intrathecal injection at the same neonatal time points of 8% DMSO vehicle (nv), and neonatal incision with vehicle (nvIN) or SB203580 (nSBIN). Mechanical withdrawal thresholds were compared following incision 6–7 weeks later (nv-IN vs nSBIN-IN vs nvIN-IN).