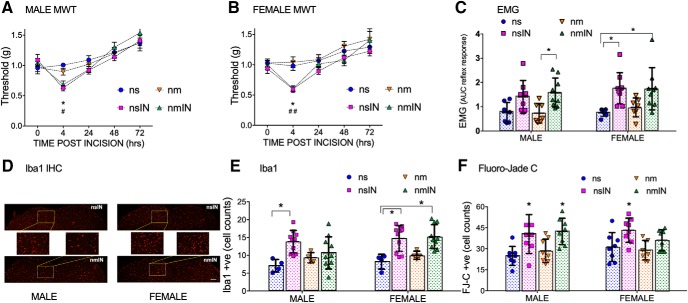
Figure 6.
Acute neonatal effects of incision and/or minocycline. A, B, Mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) is reduced 4 h following neonatal saline and incision (nsIN) in male (A) and female (B) rat pups compared with nonincised saline (ns) and minocycline (nm) controls. Minocycline at the time of neonatal incision (nmIN) has no effect. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 6 ns animals, n = 10 all other groups). ns vs nsIN: *p < 0.05; ns vs nmIN: ##p < 0.01; #p < 0.05; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc comparisons. C, Twenty-four hours following P3 interventions, reflex sensitivity was quantified as the area under the curve of the stimulus (von Frey hair to hindpaw) versus biceps femoris EMG response. Data points represent individual animals (n = 7–9 per group). Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Male nmIN > ns, p = 0.043; nmIN> nm, p = 0.035; female nsIN > ns, p = 0.007; nmIN> ns, p = 0.008; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc comparisons. D, Representative low- and high-power images of the dorsal horn of male and female rats 3 d following incision with perioperative saline (nsIN) or minocycline (nmIN). Scale bar, 210 μm. E, Iba1-positive cells within a fixed ROI in the medial superficial dorsal horn were significantly increased following incision in males (ns vs nsIN, p = 0.007), and females given saline (ns vs nsIN, p = 0.011) or minocycline (ns vs nmIN, p = 0.005). Data points represent average of at least 6 spinal L4/5 sections for each individual animal (n = 4 ns or nm; n = 10 nsIN or nmIN). F, FJ-C-positive cell counts in the ipsilateral (left) lumbar cord (L4,5 segments) were increased following incision in males (ns vs nsIN, p = 0.008; ns vs nmIN, p = 0.002; nm vs nmIN, p = 0.024) and females (nm vs nsIN, p = 0.019). Data points represent sum of FJ-C-positive counts from 6 L4/5 spinal cord sections per animal (n = 8 animals per group). E, F, Error bars indicate SD. *p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc comparisons. Groups are as follows ns, nm, nsIN, and nmIN.