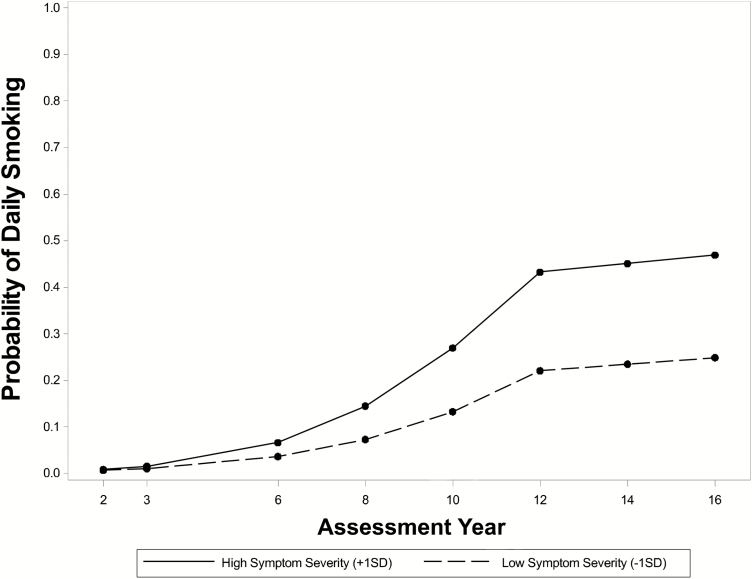
Figure 2.
Model-implied probabilities of daily smoking for high and low levels of time-varying ADHD symptom severity, 2- through 16-year assessments, for the childhood ADHD group. +1SD = one standard deviation above mean symptom severity, −1SD = one standard deviation below mean symptom severity. At any given assessment point, higher-than-usual symptom severity predicts a shift to a trajectory on which daily smoking is more likely.