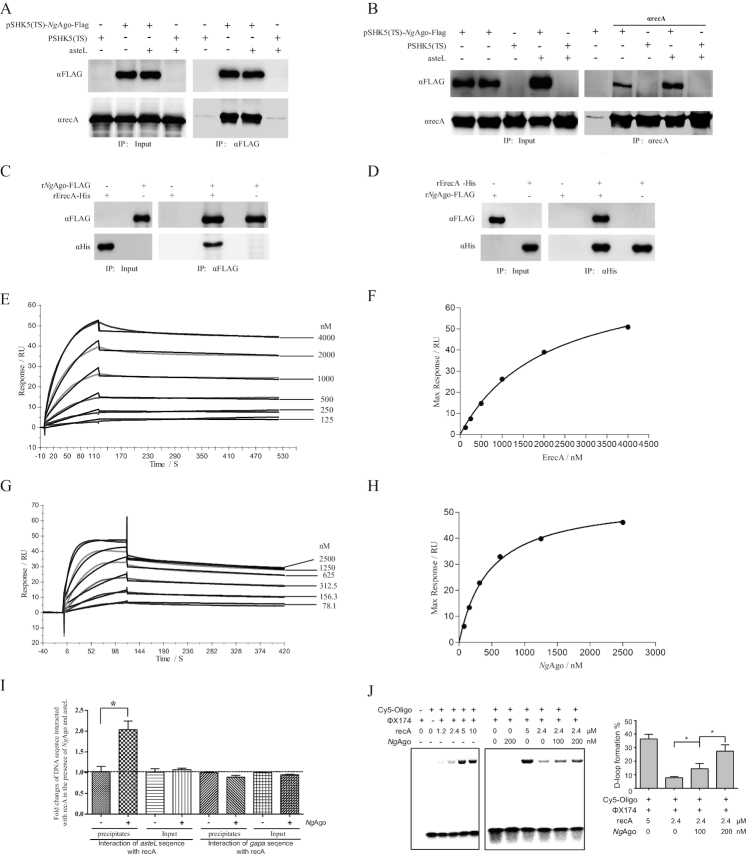
Figure 3.
NgAgo interacts with recA and enhances recA-mediated DNA strand exchange in bacteria. (A) Co-IP assay detection of the interaction between NgAgo-FLAG and endogenous recA with αFLAG agarose. The E. coli strain was transformed with pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo-Flag-asteL (the left arm sequences of aste gene), pSHK5(TS)-asteL, pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo-Flag or pSHK5(TS) and cultured for 48 hours. Total proteins were extracted for Co-IP assay with αFLAG agarose. (B) Co-IP assay detection of the interaction between NgAgo-FLAG and endogenous recA with SPA/G agarose and αrecA. The E. coli strain was transformed with pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo-Flag-asteL, pSHK5(TS)-asteL, pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo-Flag or pSHK5(TS) and cultured for 48 h. Total proteins were extracted for Co-IP assay with SPA/G agarose and αrecA. (C) Direct interaction between the purified recombinant NgAgo-FLAG with the purified recombinant ErecA-His with αFLAG agarose. The eluted proteins were further subject for immunoblot with antibodies against recA or FLAG. (D) Direct interaction between the purified recombinant NgAgo-FLAG with the purified recombinant ErecA-His with Ni-NTA agarose. The eluted proteins were further subject for immunoblot with antibodies against recA or FLAG. (E) The curves representing the binding of purified rErecA-His to rNgAgo-His. rNgAgo-His and BSA were immobilized by amine coupling to each flow cell, and different concentrations (0-4 μM) of rErecA was injected over the flow cells for surface plasmon resonance analysis. Data were obtained as response value of rErecA-His to rNgAgo-His subtracting response value of rErecA-His to BSA. (F) The plotting of the RUmax at each concentration of rErecA for rNgAgo-His. These curves were fitted to the one-binding site model, giving values for KD constants. (G) The curves representing the binding of purified rNgAgo-His to rErecA-His. rErecA-His and BSA were immobilized by amine coupling to each flow cell, and different concentrations (0–2.5 μM) of rNgAgo-His was injected over the flow cells for surface plasmon resonance analysis. Data were obtained as response value of rNgAgo-His to rErecA-His subtracting response value of rNgAgo-His to BSA. (H) The plotting of the RUmax at each concentration of rNgAgo-His for rErecA. These curve was fitted to the one-binding site model, giving values for KD constants. (I) Enhanced binding of recA with the target DNA by NgAgo. The E. coli strain was transformed with pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo-Flag-asteL or pSHK5(TS)-asteL and cultured for 12 h, then cross-linked with formaldehyde. After sonication, the lysate was precipitated with SPA agarose and αrecA. After reverse crosslinking the samples, the samples were used for qPCR detection of asteL with the aste-RT-F/R primers or the irrespective gapa sequence with the gapa-RT-F/R primers. The reca sequence was used as an internal control for qPCR with the reca-RT-F/R primers. (J) NgAgo-assisted gene editing is through enhancing recA-mediated DNA strand exchange. DNA strand exchange assay was performed based on the phiX174 RF1 DNA and HPLC-purified phiX174-oligo chemically labeled with Cy5 in the presence of rErecA and various concentration of rNgAgo-His. The products were resolved on a 1% agarose gel, and the D-loop formation and free of Cy5-labeled oligos were imaged on a Fujifilm FLA-5100 (FUJIFILM Life Science, Japan). The D-loop formation % is the percentage of the signal of the D-loop formation of Cy5-labed oligos in the signal of the D-loop formation and free of Cy5-labeled oligos.