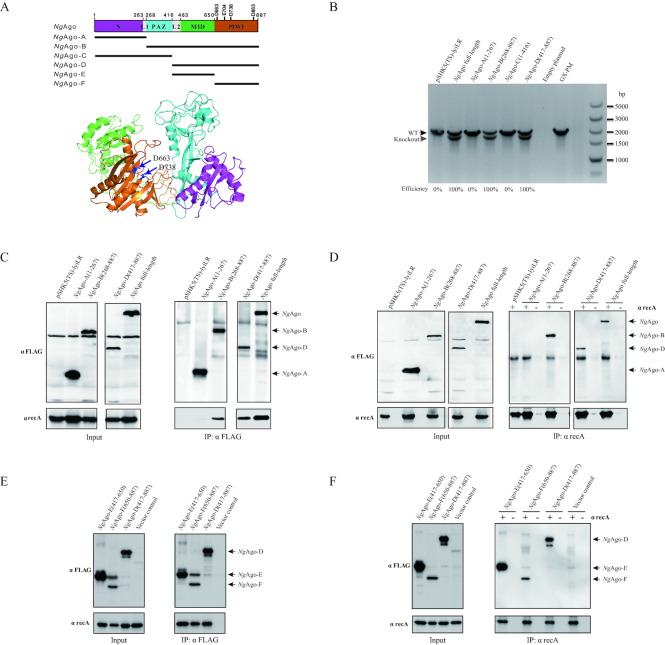
Figure 4.
The PIWI-like domain of NgAgo is required for promotion of gene editing in bacteria. (A) The structural homology modelling of NgAgo major domains aligned to Aquifex aeolicus Argonaute (PDB: 1YVU) and Thermus thermophilus Argonaute (PDB: 5XOU) using the HHPred server and Pymol. N, L, PAZ, MID and PIWI domains are highlighted in purple, grey, blue, green and orange, respectively. The structure of other pAgos were supplied in Figure S11. (B) Comparison of the construction efficiency for the isogenic lyi mutant in the P. multocida strain GX-PM based on various NgAgo fragments: A (1-267), B (268-887), C (1–416) and D (417–887). (C) Co-IP assay detection of interaction between recA and the various NgAgo fragments with αFLAG agarose. The E. coli strain was transformed with pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo (A, B or D)-Flag-asteL or pSHK5(TS)-asteL and cultured for 48 h. Total proteins were extracted for Co-IP assay with αFLAG agarose. (D) Co-IP assay detection of interaction between recA and the various NgAgo fragments with SPA/G agarose and αrecA. The E. coli strain was transformed with pSHK5(TS)-NgAgo (A, B or D)-Flag-asteL or pSHK5(TS)-asteL and cultured for 48 h. Total proteins were extracted for Co-IP assay with SPA/G agarose and αrecA. (E) Co-IP assay detection of interaction between recA and the MID domain (fragment E) or PIWI-like domain (fragment F) of NgAgo with αFLAG agarose. The fragment D of NgAgo and the vector were severed as the positive and negative controls. (F) Co-IP assay detection of interaction between recA and the MID domain (fragment E) or PIWI-like domain (fragment F) of NgAgo with SPA/G agarose and αrecA. The fragment D of NgAgo and the vector were severed as the positive and negative controls.