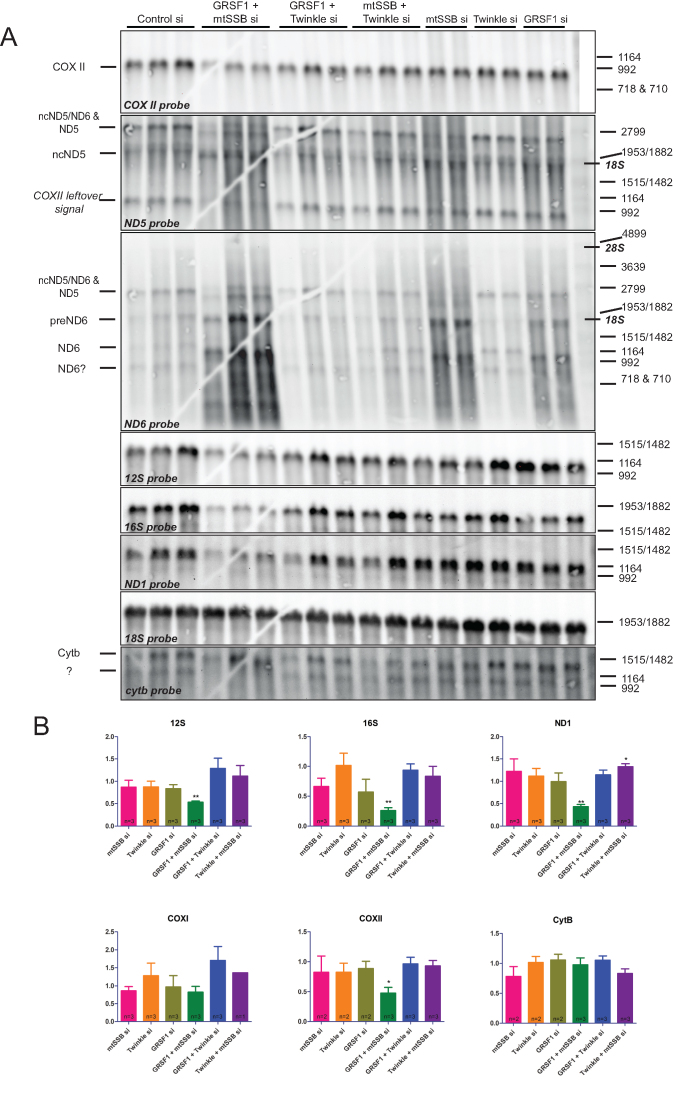
Figure 7.
An mtSSB-GRSF1 double knockdown shows an exacerbated phenotype with rRNA depletion, RNA processing abnormalities and accumulation of degradation products. Northern blot analysis was done on three biological repeats and several technical variations to exclude gel and blot artifacts and to allow for the informed assignment of RNA species (see main text). (A) Images for the seven mitochondrial probes used here (COXII, ND5, ND6, 12S rRNA, 16S rRNA, ND1 and CYTB). A repeat blot on which the order of the ND5 and ND6 probe hybridizations was inverted and on which for example also the COXI probe was used (see quantification in B) is shown in Supplementary Figure S5. Markers show denatured commercial DIG labeled DNA markers (see M&M), that nonetheless are also good RNA size markers as shown by the localization of 18S and 28S rRNA (indicated in italic-bold on the right) in relation to the marker bands. Probe hybridizations were done in the order by which we show the panels, from top to bottom. For further information on the assignment of RNA species, see the main text. RNA species are indicated by their generic names, and as either non-coding (nc) for the antisense RNA from the non-template strand or as precursor (pre). Quantification of signal after correction for 18S ribosomal RNA as a loading control, used two blots for 12S, 16S and ND1, and one blot for the other probes (B). As for Figure 2, error bars show ± SEM. Statistics used one sample t-test comparing each sample to its own control that was set at 1 (not shown in the graphs). * indicates a P-value ≤ 0.05; ** indicates a P-value ≤ 0.01. Please note that the gel-crack that is visible on this particular Northern blot (A) occurred after the gel-run prior to blotting and thus has not affected the gel-run itself and is not a cause for the altered mobility of some RNA species.