Figure 3.
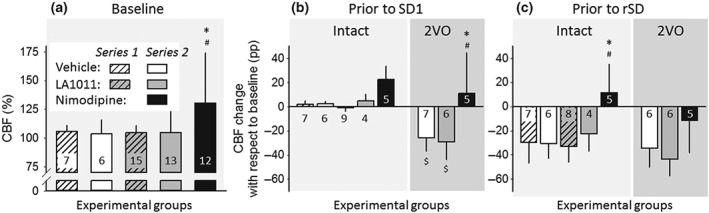
Variation of baseline cerebral blood flow (CBF; i.e., inbetween stimulations) with respect to pharmacological treatments. (a) CBF prior to the first experimental intervention (i.e., production of spreading depolarization [SD] in Series 1, or induction of ischaemia in Series 2). In Series 2, the intact group and the group of animals later undergoing bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (2VO) are merged, because they received identical handling until this point of the experimental protocol. (b) CBF before the production of the first SD (SD1). Data are expressed as change with respect to the corresponding baseline. (c) CBF before the production of recurrent SD events (rSD). Data are given as mean ± stdev; sample size (i.e., number of animals) is indicated in each bar. Statistical analysis relied on a two‐way ANOVA paradigm (factors: acute/chronic and treatment), Panel (a), or a three‐way ANOVA (acute/chronic, ischaemia, and treatment), Panels (b) and (c). The level of significance was defined as *P < 0.05. Tukey's HSD post hoc test was applied for group comparisons (*P < 0.05 vs. vehicle; # P < 0.05 vs. LA1011; $ P < 0.05 vs. respective intact)
