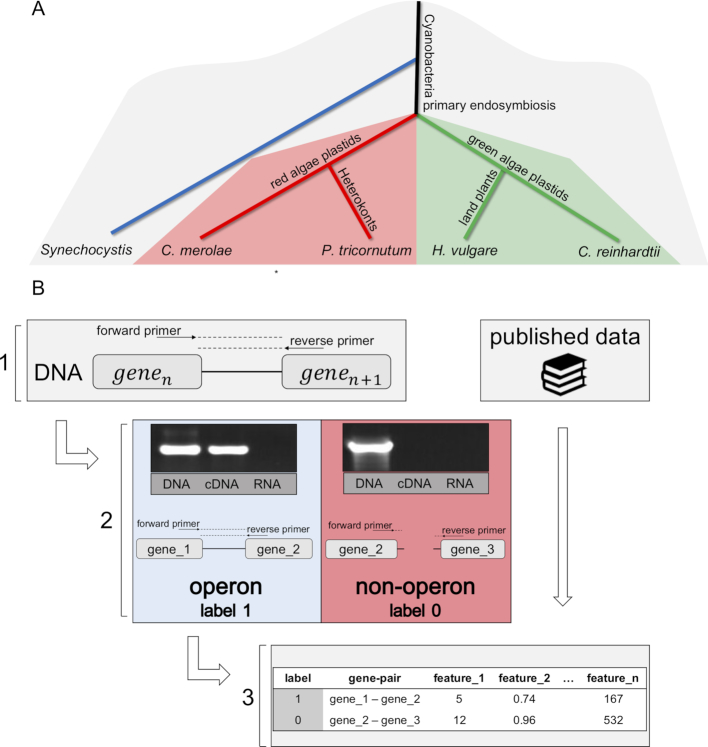
Figure 1.
The creation of a generalist dataset of plastid operons comprised of distinct evolutionary organisms. (A) Phylogenetic tree of the plastomes and genomes used to train and test the model (based on (61)); (B) The main pipeline sketch; 1. Primer design for chosen gene pairs; 2. RT-PCR analysis—the DNA template is used to verify that the primers function properly, the RNA template is used to rule out DNA contamination in the cDNA samples and the cDNA reports on the transcription state of the pair (OP or NOP); 3. Sequence-based features are computed for each gene pair. Alternatively, known operon data are retrieved and their sequence-based features are directly computed.