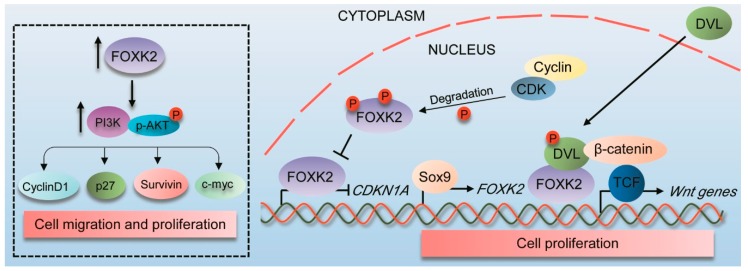
Figure 4.
FOXK2 role as an oncogene in cancer. FOXK2 is transcriptionally regulated by the Sox9 oncogene and promotes proliferation of colorectal cancer cell lines. In this context, FOXK2 interacts with DVL, translocating it to the nucleus, and then promoting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In agreement, FOXK2 overexpression promotes cell migration and proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma, which is associated with high levels of Survivin, c-Myc, p27, cyclin D1 and phosphorylated AKT protein expression. A role in cell cycle progression has also been attributed to FOXK2, which is phosphorylated by CDK-cyclin complexes in a cell cycle dependent manner, in a process that induces its degradation and impairs its transcriptional activity following cell division. Box represents associations between FOXK2 and other molecules in studies involving overexpression and inhibition of FOXK2. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; Cyclin D1, regulator of cell cycle progression; p27, a cell cycle inhibitor; Survivin, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) family; c-myc, proto-oncogene transcription factor; DVL, Dishevelled; Sox9, the sex-determining region Y box 9; TCF, T-Cell Factor; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; CDKN1A, gene encoding p21, a cell cycle inhibitor; P, phosphorylation site.