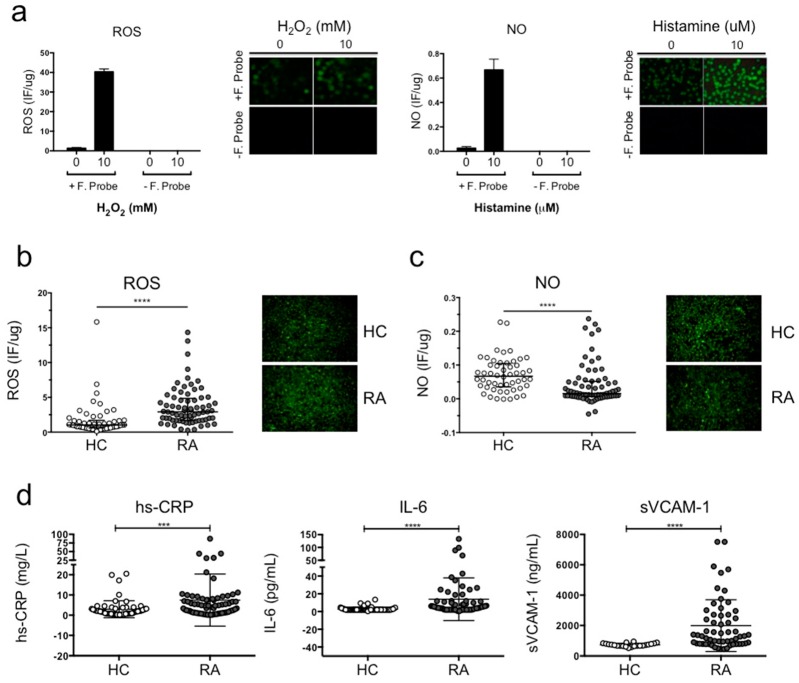
Figure 1.
Plasma from RA patients induced increased ROS production and reduced NO synthesis compared to healthy volunteers. (a) ECV-304 cells were cultured with 2.5 μM DCF for ROS and 5 μM DAF-2DA for 30 min at 37 °C 5% CO2 in 199 media. The baseline for fluorescence intensity was determined using ECV-304 cells without stimulation. The positive fluorescence signal was obtained using 10 mM H2O2 stimulation for intracellular ROS and 10 μM histamine stimulation for intracellular NO. (b) ROS production and (c) NO synthesis was measured in ECV-304 cells cultured with plasma from RA patients and healthy volunteers after 12 h of incubation. Fluorescence intensity was measured using a microplate reader at emission 540 nm (excitation 485 nm) and confirmed by fluorescent microscope. (d) Protein concentration of hs-CRP, IL-6 and sVCAM-1 in plasma from RA patients and healthy controls was measured using a chemiluminescent immunometric solid phase assay and ELISA. Mann-Whitney test was used to compare RA patients and healthy controls, *** P < 0.0005 and **** P < 0.0001 was considered significant.