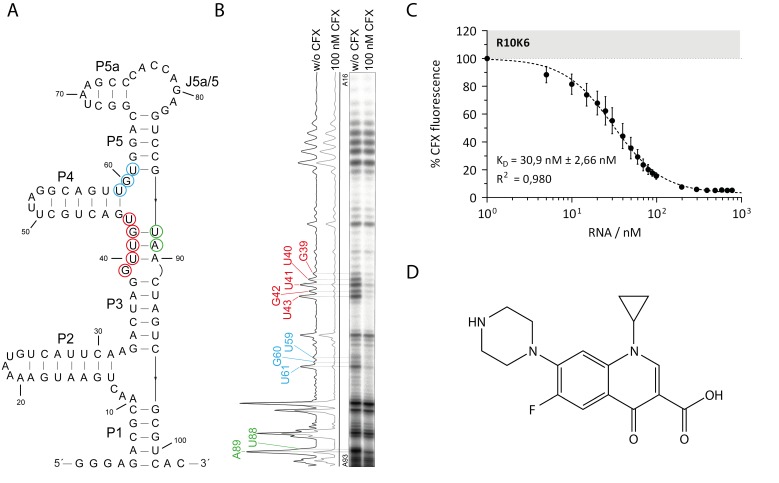
Figure 1.
Biochemical characterization of the ciprofloxacin (CFX) binding aptamer R10K6. (A) Predicted secondary structure of R10K6 by mfold [19,20,21], the six stem regions and one single-stranded region are marked with P1-P5a and J5a/5, respectively. Nucleotides with changes in the cleavage pattern are encircled and color-coded. (B) In-line probing experiment of the CFX binding aptamer R10K6. The cleavage pattern and the respective quantification is shown in the absence (w/o CFX) and presence (100 nM CFX) of CFX. Regions with changes in the cleavage pattern are marked and color-coded. (C) Fluorescence titration spectroscopy for R10K6 with CFX as ligand. The experiment was performed three times and mean and standard deviation are shown respectively (D) Chemical structure of CFX [22].