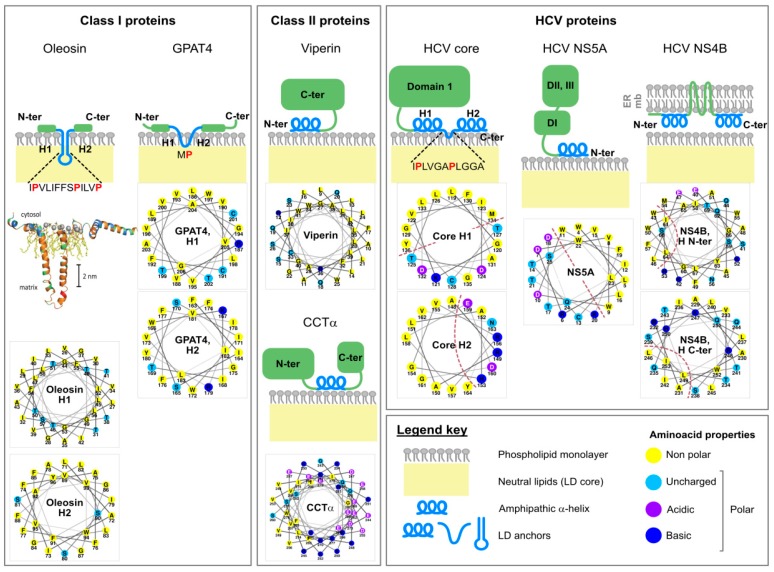
Figure 2.
Different ways to bind lipid droplets. Presumed topology of representative host and viral lipid droplet-binding proteins: P. patens plant oleosin, drosophila GPAT4 [39], mouse viperin [49], human CCTα [57], HCV core (genotype 1a strain Glasgow) [45], NS5A (consensus sequence) [47], NS4B (genotype 1b strain O) [56]. Wheel representations of the predicted or confirmed α-helices were drawn with Netwheels (http://lbqp.unb.br/NetWheels/) [58]. Dashed brown lines where assigned by the authors (where relevant) and indicate the boundary between hydrophobic and hydrophilic portion of the helix. The secondary structure of oleosin represented on the lipid droplet surface was based on homology modeling and is reproduced from Huang et al. [38] with permission of the authors and of the American Society of Plant Biologists (permission obtained via Copyright Clearance Center).