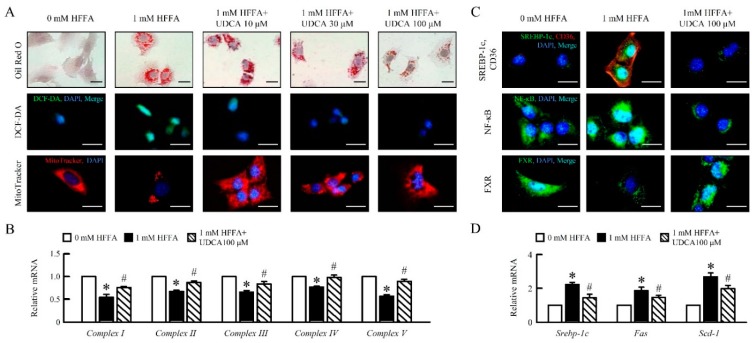
Figure 1.
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) alleviates high free fatty acid (HFFA)-induced hepatocyte lipogenesis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and mitochondrial dysfunction in AML12 cells. AML12 cells were treated with 1 mM HFFA with 10, 30, 100 μM UDCA. (A) Lipid accumulation display using Oil Red O stain (red). ROS levels were measured using DCFH-DA (green) stain. Images of AML12 cells stained with Mito Tracker for mitochondria (red). qRT-PCR analysis of (B) Complex I, II, III, IV, and V mRNA expression in AML12 cells. Relative mRNA expression was normalized to Gapdh and then normalized to the controls. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of SREBP1c (green), CD36 (red), NF-κB (green), and FXR (green) expression, and DAPI (blue) for nuclear. Scale bar, 25 μm. qRT-PCR analysis of (D) Srebp-1c, Fas, and Scd-1 mRNA expression in AML12 cells. In all panels, results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. of five independent experiments, and statistical significance of differences between means was assessed using an unpaired Student’s t-test (* p ≤ 0.05; 0 mM HFFA vs. 1 mM HFFA. # p ≤ 0.05; 1 mM HFFA vs. 1 mM HFFA+ 100 μM UDCA). UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; HFFA, high free fatty acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SREBP-1c, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; CD36, cluster of differentiation 36; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; Fas, fatty acid synthase; Scd-1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.