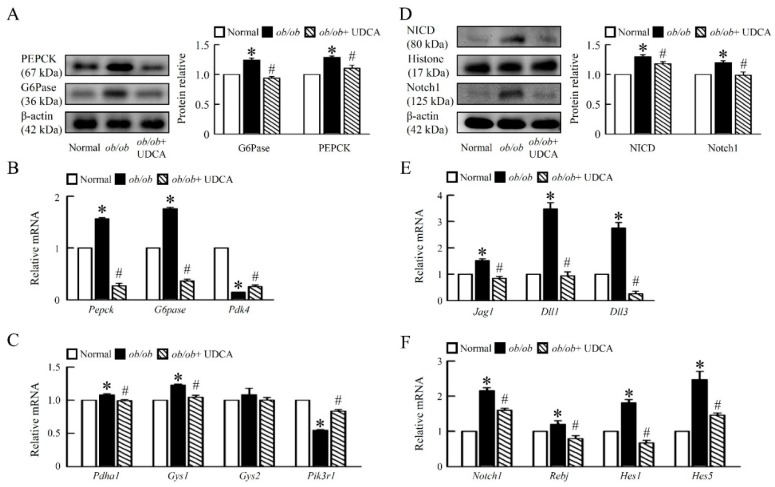
Figure 3.
UDCA reduces hepatic Notch1 signaling and glucose metabolism disorders in ob/ob mice. Normal and ob/ob mice were treated with or without 50 mg/kg UDCA for 14 days. (A) Western blot analysis of PEPCK and G6Pase protein levels in liver. qRT-PCR analysis of (B) Pepck, G6pase, Pdk4, (C) Pdha1, Gys1, Gys2, and Pik3r1 mRNA expression in liver. (D) Western blot analysis of NICD and Notch1 protein levels in liver. qRT-PCR analysis of (E) Jag1, Dll1, Dll3, (F) Notch1, Rbpj, Hes1, and Hes5 mRNA expression in liver. Relative mRNA expression was normalized to Gapdh and then normalized to the controls. In all panels, results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. of five independent experiments, and statistical significance of differences between means was assessed using an unpaired Student’s t-test (* p ≤ 0.05; normal vs. ob/ob. # p ≤ 0.05; ob/ob vs. ob/ob + UDCA). PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; G6Pase, glucose 6-phosphatase; Pdk4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; Pdha1, pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha 1; Gys, glycogen synthase; Pik3r1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit 1; Notch1, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; Jag1, Jagged1; Dll, delta like canonical Notch ligand; Rbpj, recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless; Hes, hairy and enhancer of split.