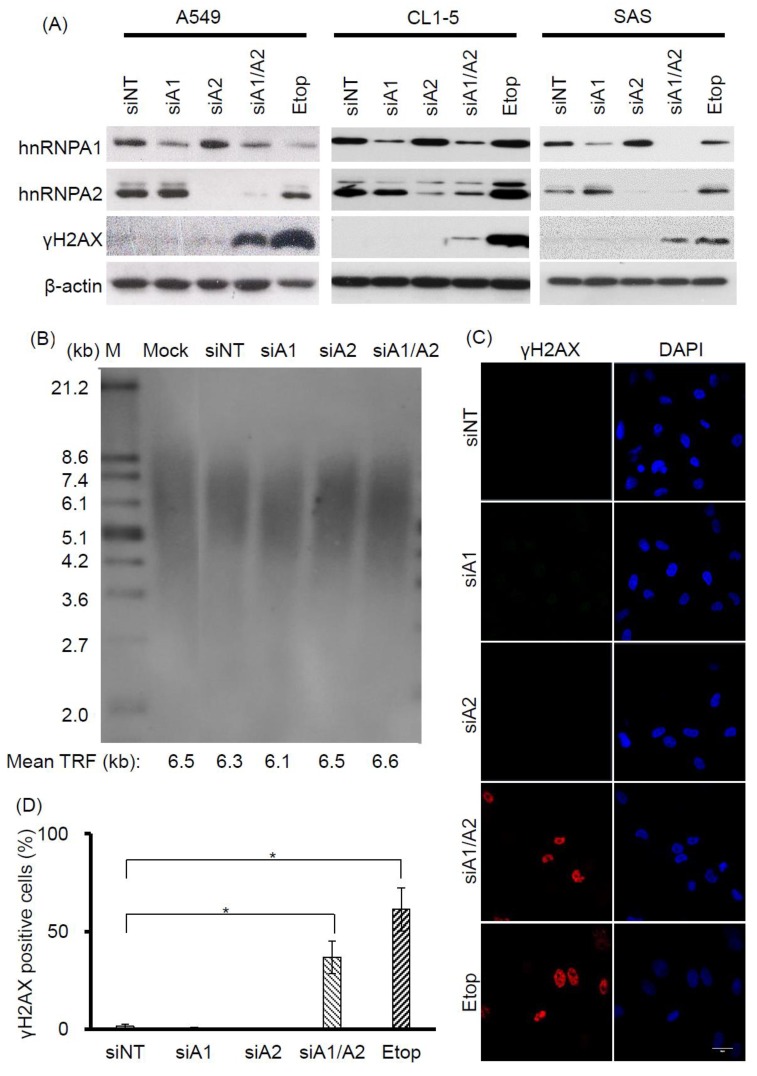
Figure 1.
Effects of depleting hnRNP A1 and/or hnRNP A2 on induction of DNA damage response (DDR). (A) Induction of γH2AX. A549, CL1-5, and SAS cells were transfected with siRNA targeting hnRNP A1 (siA1), hnRNP A2 (siA2), both hnRNP A1 and A2 (siA1/A2), or with a non-targeting sequence (siNT) for 72 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for expression levels of hnRNP A1, hnRNP A2, and γH2AX by western blotting. β-Actin served as a loading control, and cells treated with 50 μM etoposide (Etop) for 12 h served as a positive control; (B) Effect of depleting hnRNP A1 and hnRNP A2 on telomere length in A549 cells. A549 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting hnRNP A1 (siA1), hnRNP A2 (siA2), both hnRNP A1 and A2 (siA1/A2), or with a non-targeting sequence (siNT) for 96 h. The genomic DNA was purified and subjected to telomeric restriction fragment (TRF) length assay, as described in the materials and methods section. Mean TRF length is indicated at the bottom of each lane. Lane M: molecular weight markers. Mock was treated with transfection reagent only; (C) A549 cells were fixed and immunostained for γH2AX (red), and nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). Cells treated with 50 μM etoposide (Etop) for 12 h served as a positive control. The scale bar equals 20 μm. (D) The percentage of nuclei showing positive staining for γH2AX was determined from an analysis of ~100 nuclei from each experiment. Positive γH2AX staining is operationally defined here as the detection of 3 or more γH2AX foci in a nucleus. Data shown are mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05 versus siNT control.