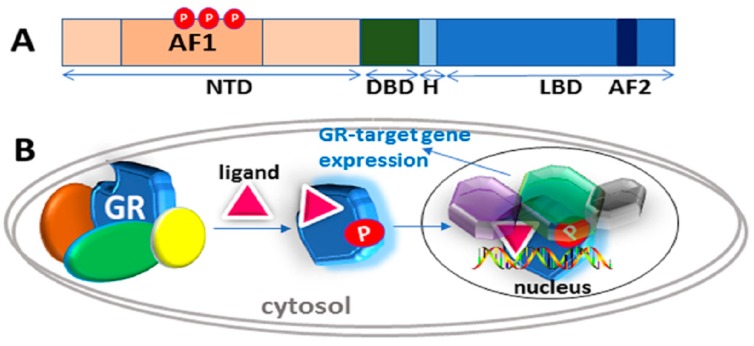
Figure 1.
Classical action of the glucocorticoid signaling mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). (A) A topological diagram of human GR protein showing major functional domains and major known AF1 phosphorylation (P) sites (other GR sites not shown) [6]. NTD, N-terminal domain; DBD, DNA binding domain; H, Hinge region, LBD, Ligand binding domain. (B) Unliganded receptor is located in the cytosol associated with several heat shock and other chaperone proteins including HSP90, HSP70, CyP-40, P23, and FKBPs (shown by different colors around GR). Ligand binding leads to conformational alterations in the GR, and by doing so GR dissociates from these associated proteins, and ligand bound GR is free to translocate to the nucleus. This process appears to be phosphorylation (P) dependent. Once in the nucleus, GR binds to site-specific DNA binding sequences and interacts with several other coregulatory proteins (shown by different colors and shapes around GR), and subsequently leads to transcriptional regulation. Based on reference [10].