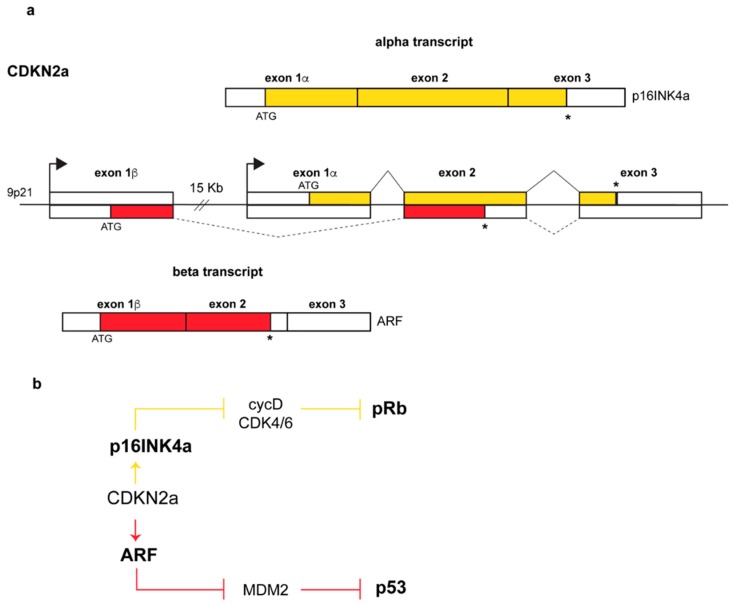
Figure 1.
Genomic structure of the CDKN2a locus and produced transcripts. (a) Arrows above each exon 1 indicate promoters, continuous and dashed lines above and below the genomic structure indicate p16 and ARF splicing patterns respectively. Transcription of exon 1β, and its splicing to exons 2 and 3 results in the α-transcript, encoding p16INK4a, whereas transcription starting upstream of exon 1β produces the β-transcript in which the exon1β, and the common exons 2 and 3 encode ARF (p14ARF in human, p19Arf in mouse). In yellow and in red are indicated the open reading frames (ORFs) of p16 and ARF respectively, with exon 2 displaying two overlapped ORFs. White boxes represent untranslated regions at the 3’ and 5’ ends while asterisks (*) indicate stop codons (b) Pathways regulated by the two proteins: while p14ARF inhibits Mdm2 (Mouse Double Minute-2) functions with consequential p53 stabilization [4,5], p16INK4a inhibits the cyclinD-CDK4/6 complex thus maintaining the retinoblastoma protein pRb in its growth-suppressive mode [4].