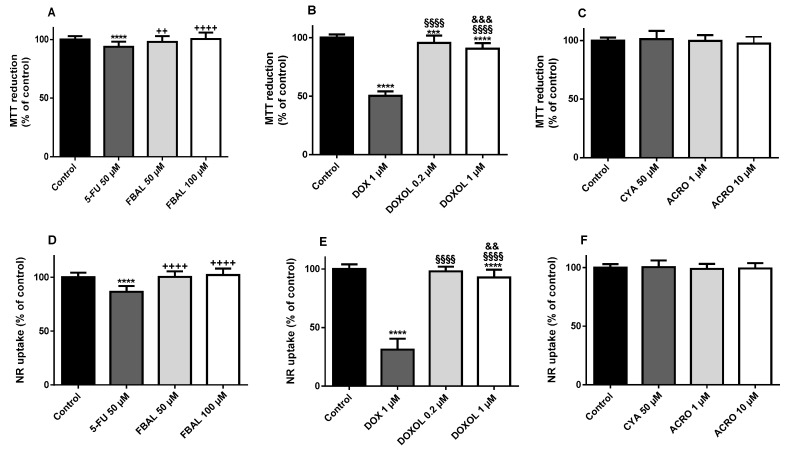
Figure 4.
Cytotoxicity evaluated by (A–C) the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction assay and (D–F) the neutral red (NR) uptake assay in differentiated H9c2 cells incubated for 48 h with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) 50 μM and α-fluoro-β-alanine (FBAL) 50 μM and 100 μM (A,D); doxorubicin (DOX) 1 μM, and doxorubicinol (DOXOL) 0.2 μM and 1 μM (B,E); and cyclophosphamide (CYA) 50 μM, and acrolein (ACRO) 1 μM and 10 μM (C,F). Results are presented as mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments (total of 20–34 wells). Statistical analyses were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by the Dunn′s post hoc test (A) or the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test, followed by the Tukey post hoc test (B–F) (*** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 vs. control; ++ p < 0.01, ++++ p < 0.0001 vs. 5-FU 50 μM; §§§ p < 0.001, §§§§ p < 0.0001 vs. DOX 1 μM; && p < 0.01, &&& p < 0.001 vs. DOXOL 0.2 μM).