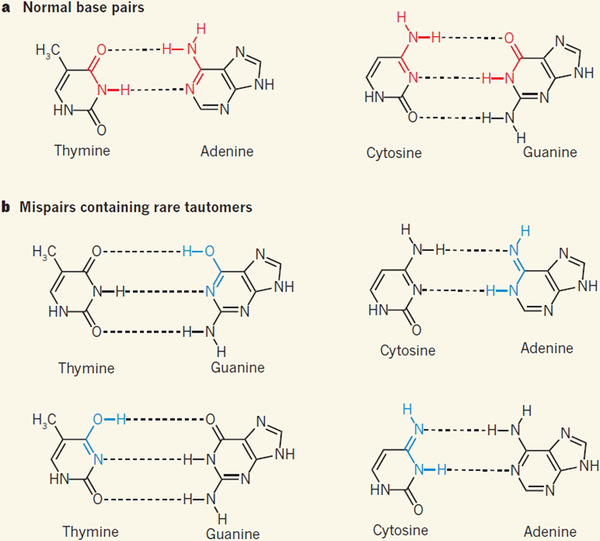
Figure 1 |. Base-pair structures in DNA.
a, The double-helix structure of DNA is held together by specific interactions (dotted lines) between pairs of bases: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C). b, The DNA bases form rare isomeric structures known as tautomers, which can allow the formation of mispairs; bonds shown in blue are the tautomeric forms of the bonds shown in red in a. Kimsey et al.1 have detected tautomeric G·T mispairs in DNA duplexes, and conclude from modelling studies that this explains the frequency with which G·T is misincorporated into DNA during DNA duplication by polymerase enzymes — as proposed3 by Watson and Crick in 1953.