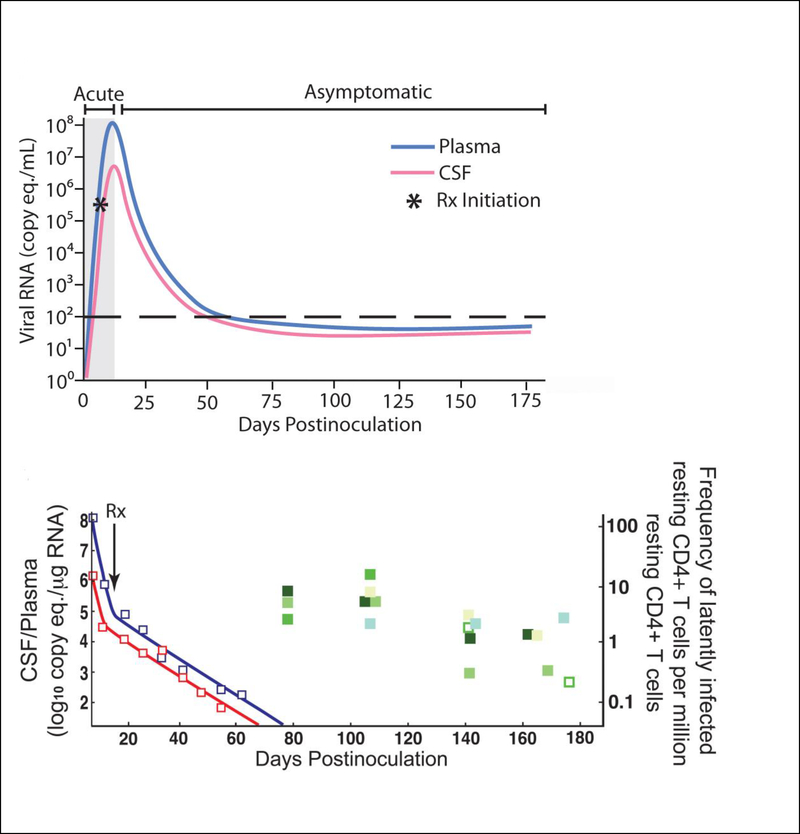
Figure 1.
(a) Viral RNA levels in plasma and CSF increase rapidly during the first 7–10 days prior to ART treatment. Within a few days after initiation of ART, plasma and CSF viral load decline. By approximately 60 days p.i., plasma and CSF viral load have declined to below the level of detection (<50 copy eq./ml) and viral loads remain low during ART. (c) The decline in plasma and CSF viral RNA occurred in two phases: an initial short-term rapid decline followed by a longer term slower decline similar to the two-phase decline seen in the plasma of HIV-infected individuals on HAART. At 80 days p.i., there were 8–10 latently infected resting CD4+ T cells per million resting CD4+ T cells in the blood. These numbers declined gradually to ~ one latently infected resting CD4+ T cells per million by 175 days p.i. Abs., absolute; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; p.i., post-inoculation; Rx, therapy; vRNA, viral RNA., plasma vRNA;, CSF vRNA (severe/moderate encephalitis);, CSF vRNA (no/mild encephalitis);, Abs. CD4+ cell counts in blood.