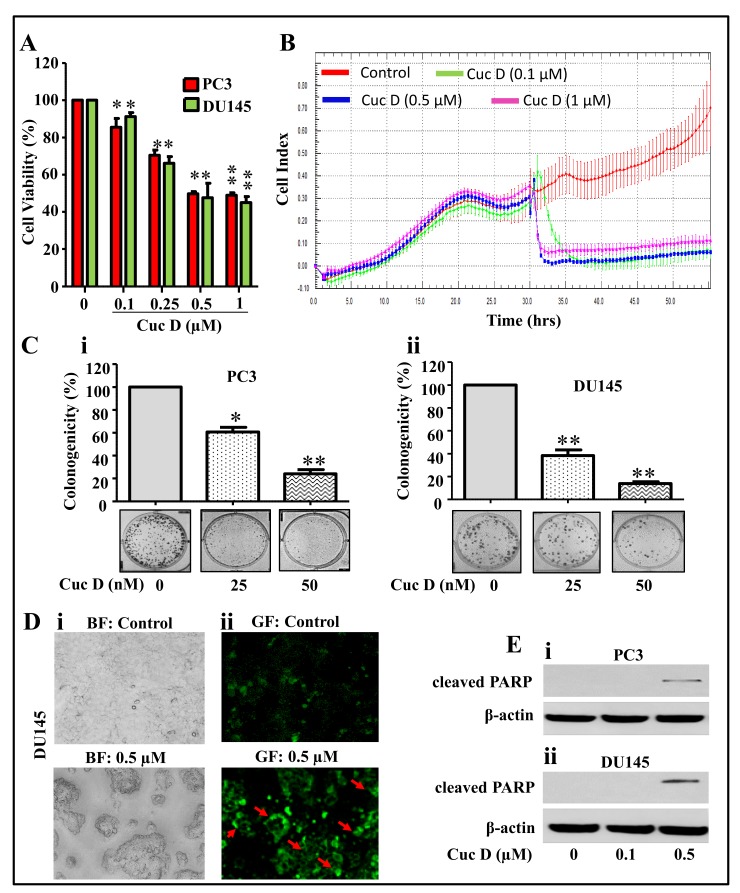
Figure 1.
Effect of Cuc D on cell proliferation, clonogenic potential and apoptosis induction in PrCa cells. (A) Effect of Cuc D on cell viability of PC3 and DU145. Briefly, cells were seeded in 96 well plate and after overnight incubation, treated with indicated concentrations of Cuc D for 48 h. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. The bar graph represents the percent viable cells compared to vehicle treated cells. Each concentration value is the mean ± SE of triplicate well of each group. Asterisk indicate statistical significance determined by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01). (B) Effect of Cuc D on cell proliferation with respect to time was also confirmed by xCelligence assay. (C) Effect of Cuc D on colony formation of PrCa cells. In brief, 500 cells were seeded in each well of 6 well plates. After 3 days, cells were treated with indicated concertation of Cuc D for 7 days and then media was replaced with complete growth media and colonies were obtained which were further stained with hematoxylin. Photographs were taken by UVP-gel documentation system for PC3 (Ci) and DU145 (Cii). Bar graph represents number of colonies formed in each group of PC3 and DU145 cells. Experiments were repeated in triplicate with similar results. Asterisk indicate statistical significance determined by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01). (D) Effect of Cuc D on apoptosis induction of DU145 cells as determined by Annexin V staining. In Brief, 0.5 × 106 cells were seeded in each well of 6 well culture plate. After 24 h, cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Cuc D and apoptosis induction was measured by Annexin V staining under fluorescent microscope. Representative images of control and Cuc D treated cells under bright field (BF) (Di) and green fluorescent (GF) (Dii). GF images (20×) represent the Annexin V stained cells as indicated by arrows. (E) Effect of Cuc D on protein levels of early apoptotic biomarker (cleaved PARP) in PC3 (i) and DU145 (ii) cells as determined by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as internal loading control.