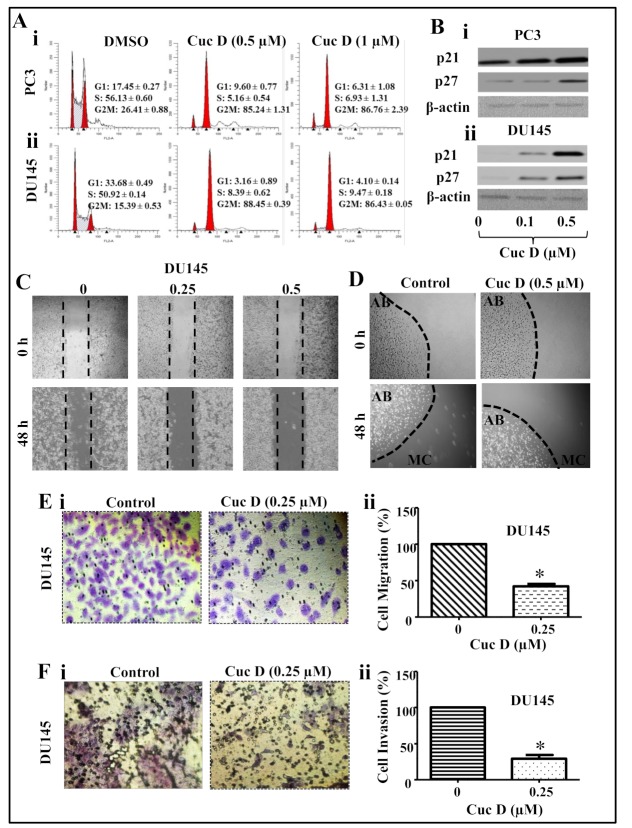
Figure 2.
Effect of Cuc D on cell cycle progression, migration and invasive abilities of PrCa cells. (A) Effect of Cuc D on cell cycle distribution in PrCa cells. Cuc D arrests PC3 (Ai) and DU145 (Aii) cell cycle in G2/M phase as determined by flow cytometry. (B) Effect of Cuc D on protein levels of cell cycle regulatory proteins (p21 and p27) in PC3 (Bi) and DU145 (Bii) cells as determined by Western blot analysis. (C–E) Effect of Cuc D on migration of PrCa cells as determined by scratch wound, bead assay and Boyden chamber assays. (C) Representative images of migratory DU145 cells in control and treated groups at 0, 48 h as determined by scratch wound assay. (D) Illustrative images of migratory cells (MC) in control and Cuc D treated groups at 0 and 48 h as determined by agarose bead assay. (E) Effect of Cuc D on migration of DU145 cells as examined by Boyden chamber assay as explained in the Materials and Methods section. In brief, 18 h post-treatment of indicated concentration of Cuc D, migrated cells were fixed and counted in control and Cuc D treated DU145 cells (Ei). Bar graph represents the quantification of migrated DU145 cells (Eii). (F) Effect of Cuc D treatment at 18 h on invasion of PrCa cells as described under materials and methods. Illustrative images (20×) of invaded control and Cuc D treated DU145 cells (Fi). Bar graph represents the quantification of DU145 (Fii) cells. Single asterisk (*) denotes the significant value p < 0.05.