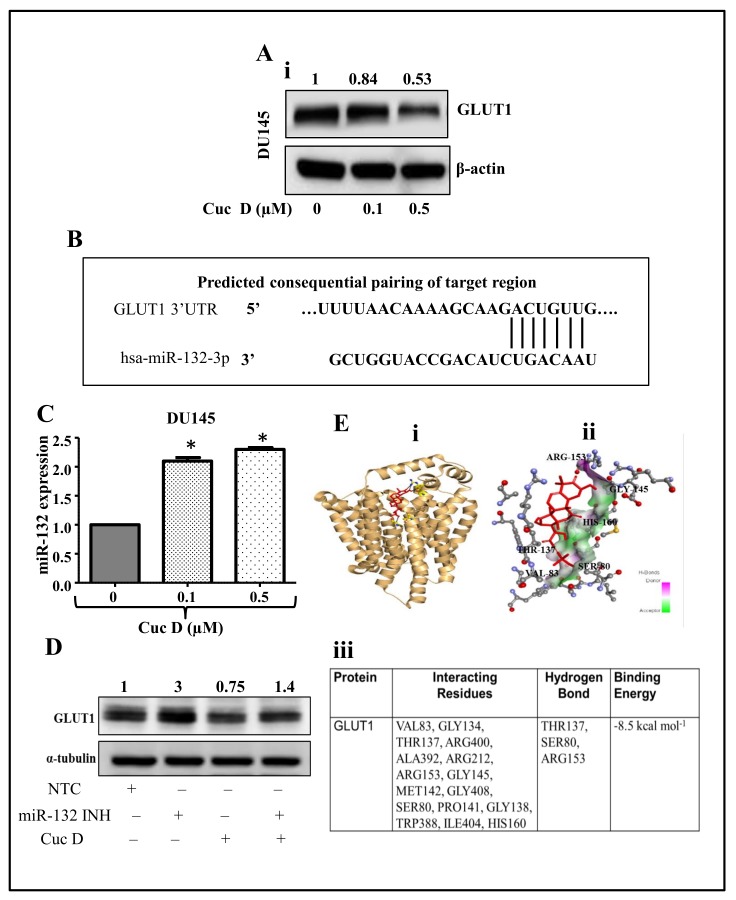
Figure 4.
Molecular mechanism of Cuc D targeting GLUT1 in PrCa cells. (A) Effect of Cuc D on GLUT1 expression in DU145 cells (A) as examined by western blot analysis. Briefly, cells were treated with denoted concentrations of Cuc D for 24 h and total cell lysates were prepared and subjected for western blot analysis for GLUT1 protein level. β-actin was used as an internal loading control. Values shown above the blot are densitometric analysis of GLUT1 blot normalized with β-actin using GelQuant software. (B) Putative miR-132 binding sites in the SLC2A1 3′UTR region of GLUT1. Seven bases (192 through 198) of the SLC2A1 3′UTR are perfect matches (seed sequences) for miR-132 binding. (C) Effect of Cuc D on the expression of miR-132 in PrCa as determined by qPCR analysis. RNU6B was used as an internal control. Asterisk (*) denotes the significant value p < 0.05 when applied student’s t-test. (D) Effect of Cuc D on GLUT 1 expression after transfection of the cells with miR-132 inhibitor as determined by western blot analysis. α-tubulin was used an internal loading control. (E) Molecular docking studies of Cuc D with GLUT1 as determined by AutoDock 4 package. Cartoon view of Cuc D docked with GLUT1 protein (Ei). Stereo view of GLUT1 binding with Cuc D, showing hydrogen bond donors and acceptors residues around components (Eii). Table depicting the GLUT1 residues interacting with Cuc D (Eiii).