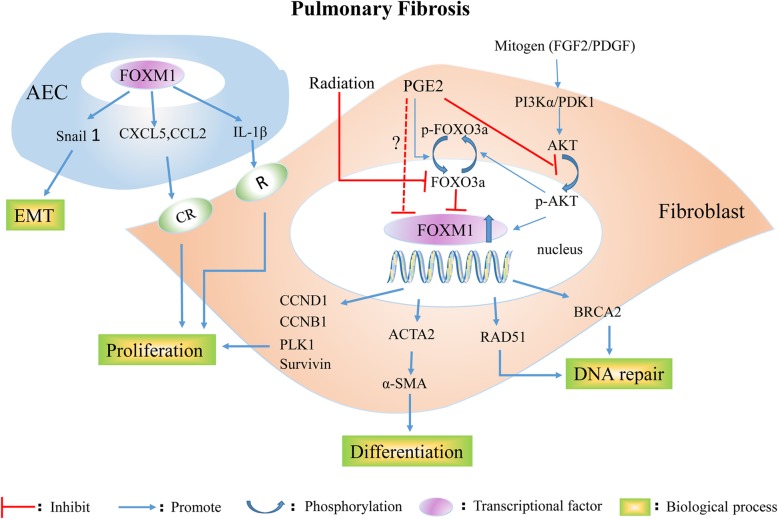
Fig. 3.
The mechanism regulation of FOXM1 in pulmonary fibrosis. In response to various stimulus, such as inflammatory mediators, radiation and mitogen, FOXM1 induces the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in alveolar type II epithelial cells, and activates fibroblasts. Elevated FOXM1 transcription in activated fibroblasts promote the fibroblast proliferation, differentiation and DNA repair, consequently accelerating the process of pulmonary fibrosis. EC: endothelial cell; SMC: smooth muscle cell; CXCL12: chemokine ligand 12; CXCR4: chemokine receptor type 4; ET-1: endothelin-1; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1; MIF: macrophage migration inhibitory factor; NBS1: Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1; PDGF-B: platelet-derived growth factor -B; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; BRCA2: breast cancer-associated gene 2