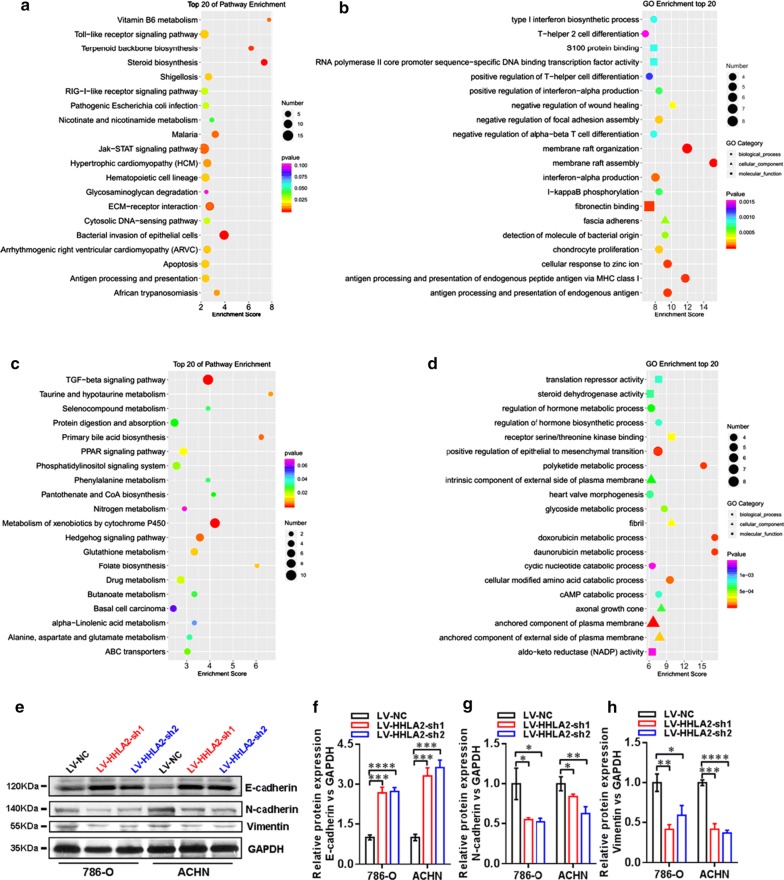
Fig. 5.
HHLA2 is potentially involved in the regulation of EMT in human ccRCC cells. We identified the differentially expressed gene profiles between LV-HHLA2-sh1 and LV-NC groups of ccRCC cell lines using microarray analysis. a, b The co-up-regulated genes were involved in the KEGG and GO analyses, and the top 20 pathways were listed, and for the co-down-regulated genes, the top 20 pathways were listed in c, d. In the following cellular study, we further examined the changes of EMT markers after HHLA2 knockdown expression in ccRCC cell lines. e Western blotting analysis of E-cadherin, N-cadherin and Vimentin in 786-O and ACHN cells in different groups. f After knockdown of HHLA2 in 786-O and ACHN, the expression of E-cadherin was significantly increased (In 786-O: LV-HHLA2-sh1 vs LV-NC: P < 0.001, LV-HHLA2-sh2 vs LV-NC: P < 0.0001; In ACHN: LV-HHLA2-sh1 vs LV-NC: P < 0.001, LV-HHLA2-sh2 vs LV-NC: P < 0.001). g After knockdown of HHLA2 in 786-O and ACHN, the expression of N-cadherin was significantly decreased (In 786-O: LV-HHLA2-sh1 vs LV-NC: P < 0.05, LV-HHLA2-sh2 vs LV-NC: P < 0.05; In ACHN: LV-HHLA2-sh1 vs LV-NC: P < 0.01, LV-HHLA2-sh2 vs LV-NC: P < 0.05). h After knockdown of HHLA2 in 786-O and ACHN, the expression of Vimentin was significantly decreased (In 786-O: LV-HHLA2-sh1 vs LV-NC: P < 0.01, LV-HHLA2-sh2 vs LV-NC: P < 0.05; In ACHN: LV-HHLA2-sh1 vs LV-NC: P < 0.001, LV-HHLA2-sh2 vs LV-NC: P < 0.0001)