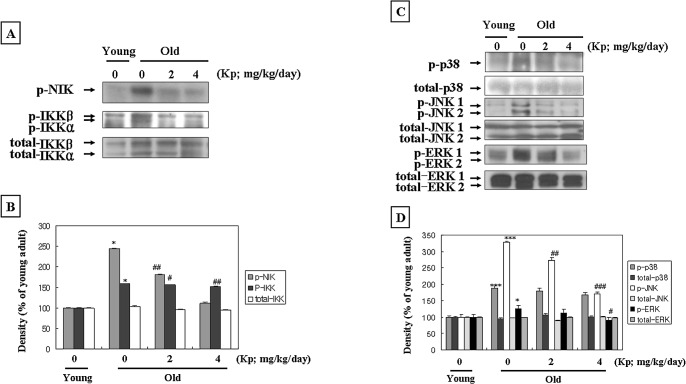
FIG. 5.
Kaempferol (Kp) inhibited the NIK/IKK and MAPKs pathways. (A) Western blot analysis was performed to detect phospho-NIK, phospho-IKKα/β, and total-IKKα/β in kidney cytoplasmic extracts (80 μg of protein) from each group. Levels were normalized to total-IKKα/β. (B) The level of protein was quantified by densitometry as a percentage of the level of the young rats. Results of one-factor analysis of variance: *P < .05 versus young rats; #P < .05, ##P < .01 versus aged rats not fed Kp. (C) Phospho-38, phospho-c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)1/2, and phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 protein levels in cytoplasmic fractions (80 μg of protein) from each group. Levels were normalized to total-p38, total JNK1/2, and total-ERK1/2. One representative blot of each protein from each group is shown from three experiments that yielded similar results. (D) The level of protein was quantified by densitometry as a percentage of the level of young rats. Results of one-factor analysis of variance: *P < .05, ***P < .001 versus young rats; #P < .05, ##P < .01, ###P < .001 versus aged rats not fed Kp.