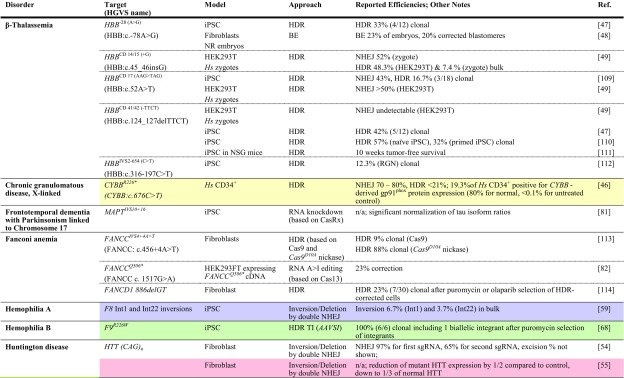
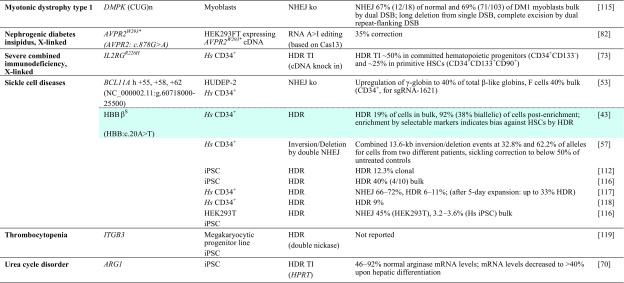
Table 1.
Achievements based on RNA-guided nuclease technology towards therapy development for rare diseases in human patient-derived cells
Reports are sorted by disease, then by gene and disease-causing mutation. All iPSCs are of human patient-derived origin. Colored fields indicate correspondence with studies in animal models in Table 2
ARG1 arginase 1, BE base editor, bulk population-wide percentages after treatment, without enrichment or antibiotic selection of corrected cells, cDNA complementary DNA, clonal percentages amongst pre-selected antibiotic-resistant clones, DM1 myotonic dystrophy type 1, DSB double-strand break, HDR homology-directed repair, HGVS Human Genome Variation Society, Hs Homo sapiens, HUDEP-2 human umbilical cord blood-derived erythroid progenitor cell line, iPSC induced pluripotent stem cell, ITGB3 integrin beta-3, ko knockout, mRNA messenger RNA, n/a not available, NHEJ non-homologous end-joining, NR embryos embryos created by fusion of thalassemic fibroblast nuclei with in vitro matured enucleated oocytes, NSG NOD (non-obese diabetic)-SCID (severe combined immunodeficient)-Il2rg-/-, TI targeted integration, zygotes tripronuclear zygotes