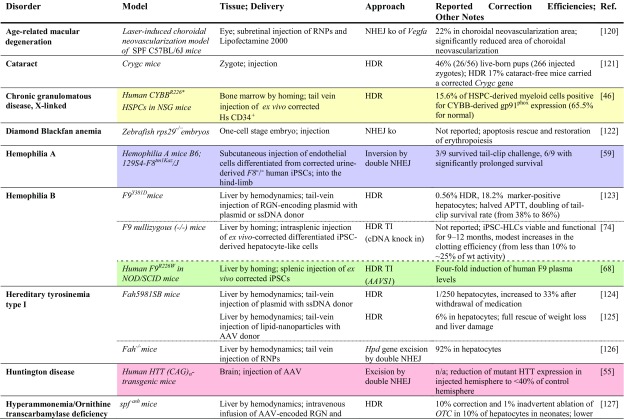
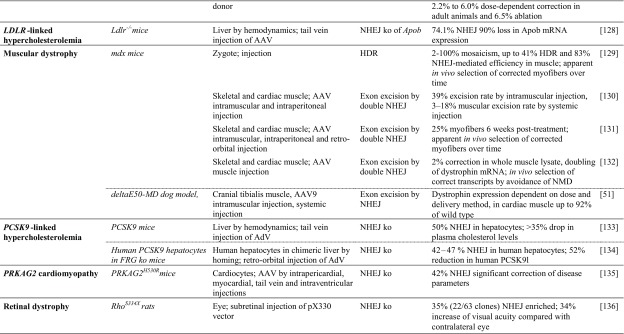
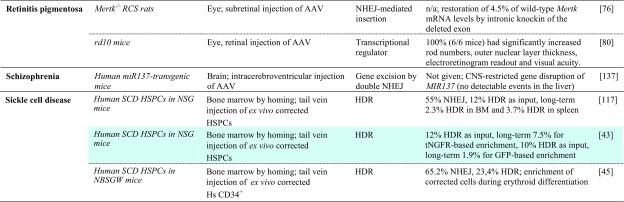
Table 2.
Achievements based on RNA-guided nuclease technology towards therapy development for rare diseases in in vivo studies
Studies listed are based on chimeric or transgenic animal disease models. Reports are sorted by disease, then by model. Percentage of ‘correction’ refers to alleles. Colored fields indicate correspondence with in vitro studies in patient-derived cells in Table 1
AAV adeno-associated virus, AdV adenovirus, APTT activated partial thromboplastin time; cDNA complementary DNA, CNS central nervous system, FRGFah–/–Rag2–/–Il2rg–/–, GFP green fluorescent protein, HDR homology-directed repair, Hs Homo sapiens, HSPC hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell, iPSC induced pluripotent stem cell, ko knockout, LDLR low density lipoprotein receptor, MIR137 microRNA 137, mRNA messenger RNA, n/a not available, NHEJ non-homologous end-joining, NOD non-obese diabetic, NSG NOD (non-obese diabetic)-SCID (severe combined immunodeficient)-Il2rg-/-, OTC ornithine transcarbamylase, PRKAG2 protein kinase AMP-activated non-catalytic subunit gamma 2, RNPs ribonucleoprotein particles, SCID severe combined immunodeficient, SPF specific pathogen-free, ssDNA single-stranded DNA, TI targeted integration, tNGFR truncated nerve growth factor receptor