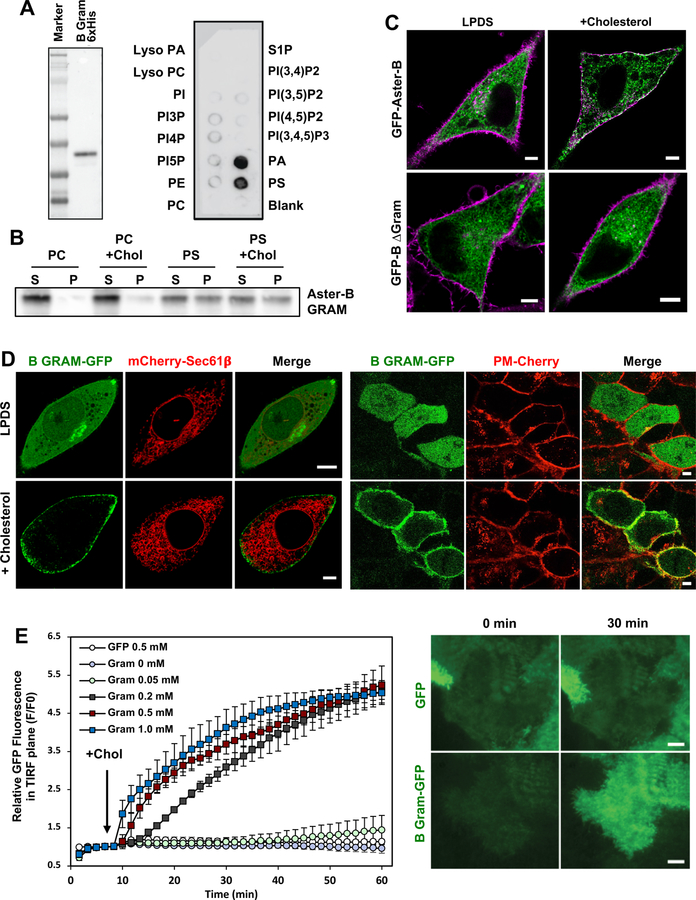
Figure 5. The GRAM domain mediates cholesterol-dependent Aster recruitment.
(A) Protein-lipid overlay of mouse Aster-B GRAM domain with various phospholipid species.
(B) Purified Aster-B GRAM domain was incubated with liposomes containing Dansyl-PE and 80–85% PC or 80–85% PS +/− 5% Cholesterol. Liposomes were sedimented, washed, and analyzed by immunoblotting for Gram domain association.
(C) Localization of full-length and B ∆GRAM Aster-B-GFP (green) constructs in HeLa cells in the presence or absence of cholesterol loading. Magenta, CellMask PM stain.
(D) Localization of B GRAM-GFP in CHO-K1 cells (left) and A431 cells (right) cultured in LPDS (top) or loaded with cholesterol (bottom). PM marker: PM-cherry; ER marker: mCherry-Sec61β. Scale bar: 5 µM. See also Supplemental Movie 2.
(E) Quantification of Aster-B PH-EGFP intensity in the TIRF plane upon cholesterol loading (left panel; n = 2–3 cells, error bars +/− SD). Representative TIRF images (right panel) from GFP and Aster-B PH-EGFP-expressing cells at the indicated time following cholesterol loading. See also Supplemental Movie S3, S4 and Supplemental Figure 4E. Results are representative at least two independent experiments.