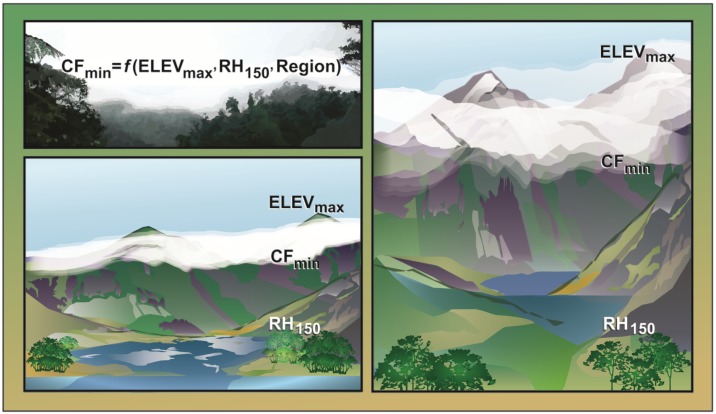
Fig 3. A simple model mapped and projected cloud forest minimum elevation (CFmin).
The model parameters include maximum watershed elevation (ELEVmax), to gauge the mass elevation effect; average annual hourly relative humidity (RH) from 100–150 m elevation within a watershed (RH150), to account for differences in the humidity of the rising air; and region (Region), to help account for other factors that affect cloud formation. All else equal, the mass elevation effect causes CFmin to be at a lower elevation on smaller mountains compared with larger ones. Also, on larger mountains, frost or atmospheric inversions occur that cause colder or drier conditions that define cloud forest upper limits, though fast-draining soils, land use, microclimate, or other factors may also define cloud forest upper limits.