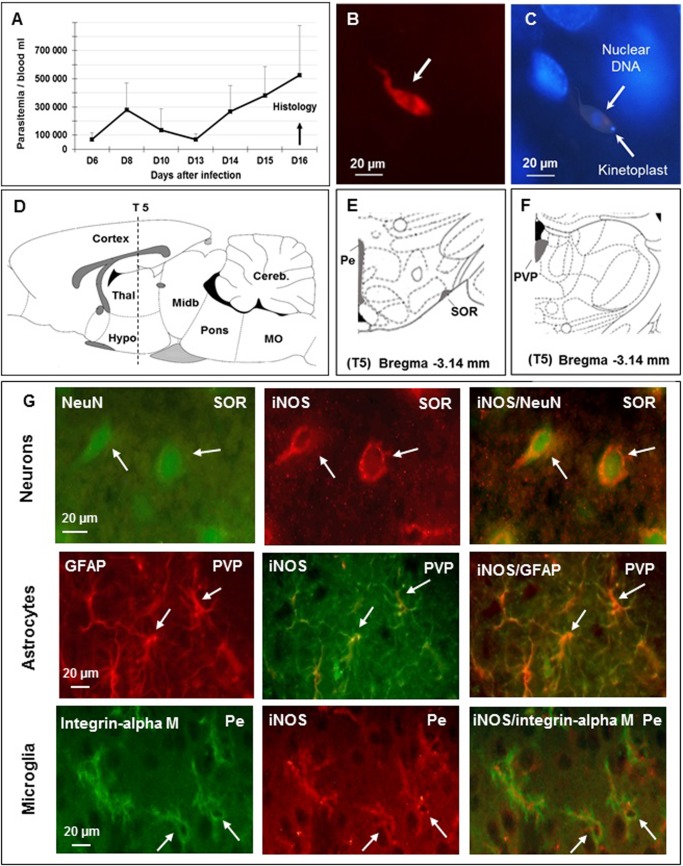
Fig 1. Identification of brain cells (neurons, astrocytes and microglial cells) expressing the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in Wistar male rats 16 days after infection with T. b. brucei.
A–Time course of parasitemia after infection (mean value ± SEM, n = 6, per day); trypanosomes appear in the blood 6 days (D6) later, corresponding to stage 1 human African trypanosomiasis (HAT); successive parasitemic waves take place; abscissae: days after infection; ordinates: parasitemia/mL. B—Immunofluorescent staining of T. b. brucei (in red, white arrow) in the brain parenchyma on D16 post-infection, corresponding to stage 2 of HAT (section S5, subfornical organ of the hypothalamus, n = 3), bregma -3.14 mm (according to reference [25]); C—Hypothalamic cell nuclei stained with DAPI (blue, subfornical organ of the hypothalamus); T. b. brucei are also stained (white arrows); D—Sagittal schema of the brain (lateral 0.4 mm / (according to reference [25]) showing the position of the 5th coronal section (S5) chosen for iNOS immunostaining; E and F—Coronal schemas at bregma -3.14 mm (according to reference[25]) showing ventral (E) and dorsal (F) diencephalon. Grey matter, containing all brain cell types, was examined; G—Cellular labelling at section S5, bregma -3.14 using specific biological markers: neurons (NeuN), astrocytes (GFAP) and microglia (integrin alpha M) were identified (left column of part G); the 3 types of cells were also iNOS-positive (medial column of part G); double labelling appears in the right column (Neurons: NeuN and iNOS; Astrocytes: GFAP and iNOS; Microglia: Integrin alpha M and iNOS). Abbreviations: T. b. brucei, Trypanosoma brucei brucei; DAPI, 4’, 6’ Di amino-2-phenylindole; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; scale is given in μm, micrometer; NeuN, neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Pe, periventricular hypothalamic n; PVP, paraventricular thalamic n, posterior part; SOR, supraoptic n, retrochiasmatic; An Olympus BX51 microscope was equipped with DP50 camera (objective 64x10).