Figure 1.
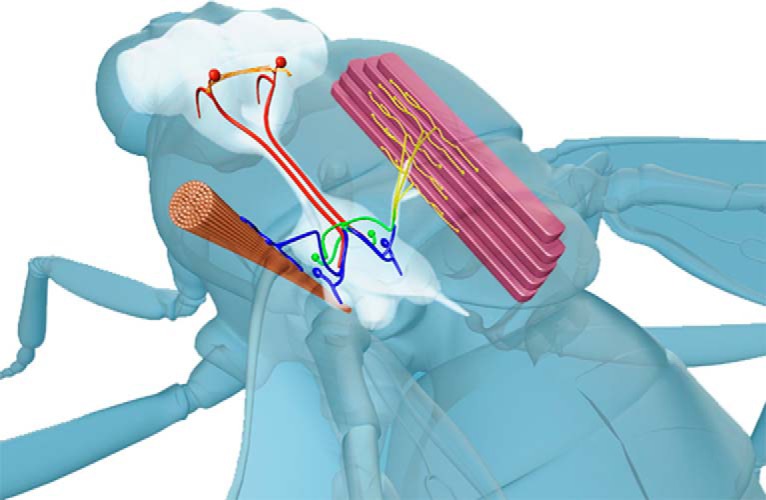
Diagram of the GFS anatomy. Two GF interneurons originating in the brain (red) descend to the thoracic ganglia where they connect, via a mixed (electrical and chemical) synapse, to the TTMn (blue) innervating the cylindrical TTM. In the second branch of the circuit, the GFs form a mixed synapse with the PSI (green), which, in turn, chemically synapses onto the DLMns (yellow) innervating the DLMs. Red circles in the brain denote approximate positions of the GF cell bodies.
