Fig. 1. Analysis of the effects of clusterin on the aggregation kinetics of Aβ(M1-42).
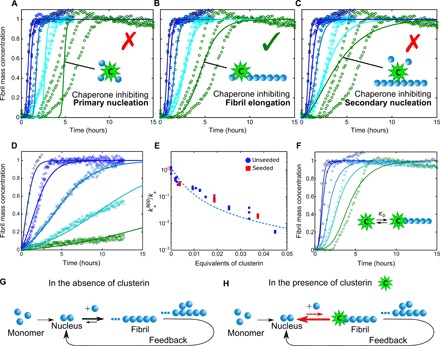
(A to C) Kinetic reaction profiles for the aggregation of 4 μM Aβ(M1-42) solutions are shown in each panel from left (blue) to right (green) in the absence and presence of 7.5, 37, 75, and 135 nM clusterin, with each color representing repetitions at the same concentration. The integrated rate law for Aβ(M1-42) aggregation in the absence of clusterin using the rate constants, previously determined by a least-squares error function, is shown as a dark blue line in each case (10). Predicted profiles of the specific inhibition processes of (A) primary nucleation, (B) fibril elongation, and (C) secondary nucleation generated by clusterin are shown as continuous lines. Note the characteristic differences in the changes in the shape of the reaction profiles in each case. The prediction for the case where the molecular chaperone suppresses only elongation events matches closely the experimental data in the presence of different concentrations of clusterin. (D) Kinetic reaction profiles for the aggregation reaction of a 2 μM Aβ(M1-42) solution seeded with 100 nM preformed fibrils in the absence and presence of 7.5, 37, 75, and 135 nM clusterin. The lines represent the integrated rate laws for Aβ(M1-42) aggregation, where the elongation rate has been selectively reduced. The apparent elongation reaction rates as a function of the molecular chaperone concentration evaluated from the fitting in (B) and (D) are reported in (E) for both unseeded and seeded reactions. The continuous line in (E) represents a simplified correlation between the elongation rate and the binding affinity constant (see Materials and Methods), from which KD,37°C = 8 nM is determined. (F) Comparison between the experimental data reported in (B) and theoretical predictions of the reaction profiles calculated from a kinetic model, which considers the association and dissociation rate constants in the reaction scheme with KD,37°C = 2.5 nM. (G and H) Schematic diagrams showing the molecular pathways involved in Aβ(M1-42) aggregation (G) and the mechanism by which clusterin perturbs the aggregation process (H).
