Fig. 4.
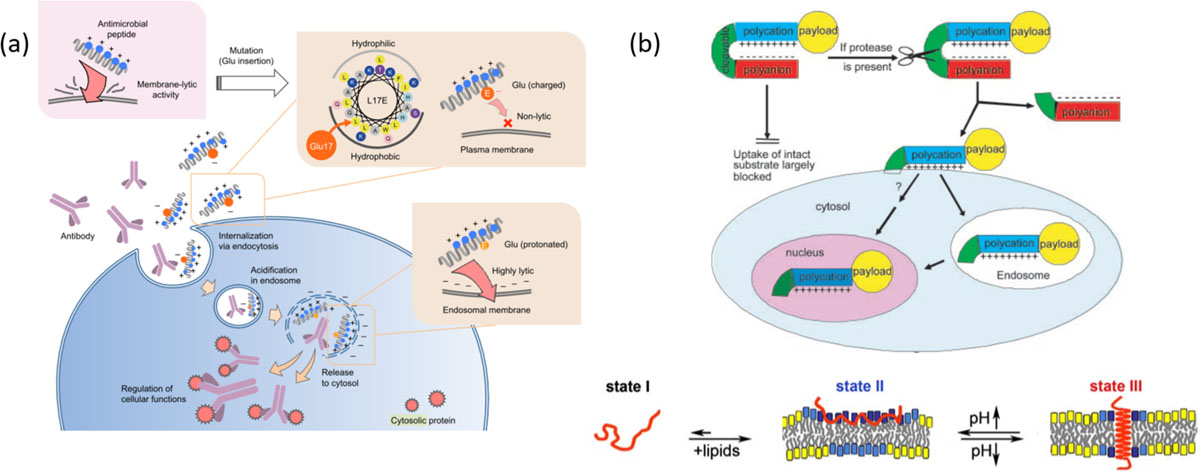
(a) Schematic illustration of design of endosomolytic peptides. The strong lytic activity of a cationic peptide was attenuated by introducing a glutamate residue into hydrophobic face. Protonation of Glu at endosomal pH enables interaction with endosomal membrane followed by membrane perturbation to release the antibodies intracellularly, reprinted with permission from [67]; (b) Activatable cell penetrating peptides or pH low insertion peptides (pHLIP) display their ability to enter cells only upon reaching target site, where protease cleavage reveals CPP in case of ACPP reprinted with permission from [73] (Copyright 2004 National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A) or conformational change observed in peptides due to acidic pH at tumor site, reprinted with permission from [74]
