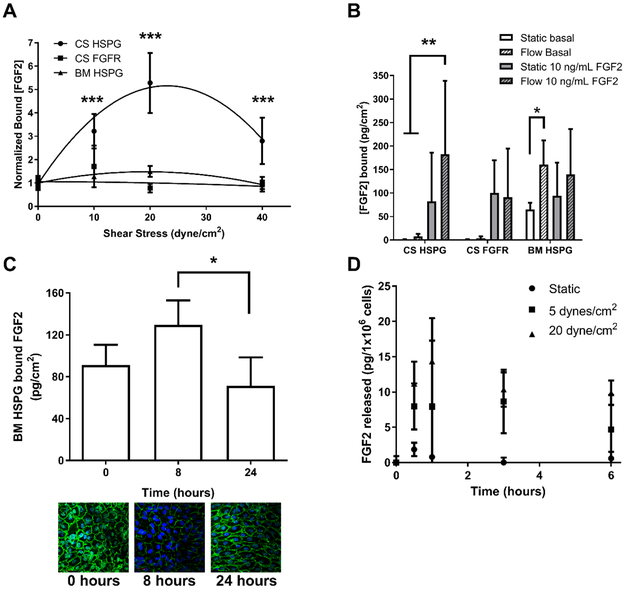
Figure 2:
FGF2 binding to cell surface and basement membrane HSPG peaks around 20 dynes/cm2 shear stress. (A) PAEC were adapted to varied shear stress levels (0 – 40 dynes/cm2) for 24 hours and then exposed to 10 ng/mL FGF2 at the same shear stress level for an additional two hours at 37°C. FGF2 bound to cell surface HSPG and FGFR, as well as basement membrane HSPG were extracted and quantified by ELISA. (B) PAEC adapted to 0 or 20 dynes/cm2 shear stress were treated with 0 (basal) or 10 ng/mL FGF2 for two hours at 37°C. FGF2 bound to cell surface HSPG and FGFR, as well as basement membrane HSPG was extracted and quantified by ELISA. (C) To assess permeability, PAEC were exposed to 0, 8 or 24 hours of 20 dynes/cm2 shear stress and then treated with 10 ng/mL FGF2. Cells were then lysed, and the FGF2 that permeated the endothelial monolayer and bound to the basement membrane was extracted and quantified by ELISA. Alternatively, cells were fixed and labeled for β-catenin (green) and nuclei (blue). (D) To assess FGF2 release from cells exposed to flow, FGF2 was quantified in media samples from PAEC exposed to 0 or 20 dynes/cm2 shear stress by ELISA. FGF2 was normalized for both media volume and cell number, and therefore is expressed as pg/1×106 cells. * p < 0.01; ** p < 0.001; *** p < 0.0001.