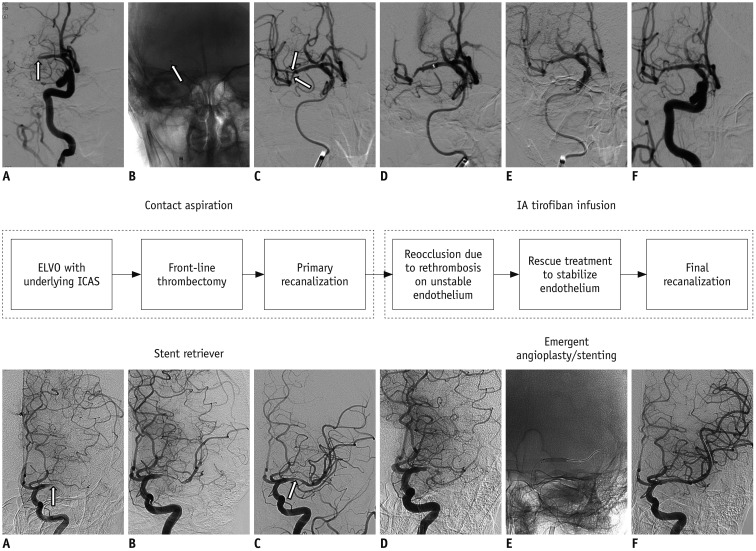
Fig. 1. Therapeutic algorithm for ELVO due to underlying ICAS.
Upper row: A. Baseline angiography shows occlusion (arrow) at distal M1 segment of right MCA. B. Contact aspiration thrombectomy using large-bore aspiration catheter. Arrow indicates tip of aspiration catheter. C. Primary reperfusion. Arrows indicate underlying atherosclerotic stenosis. D. Reocclusion and flow stagnation due to rethrombosis on irritable endothelium. E. IA infusion of tirofiban (0.5 mg) over 10 minutes. F. Final reperfusion. Lower row: A. Baseline angiography shows occlusion (arrow) at proximal M1 segment of left MCA. B. Stent-retriever thrombectomy. C. Primary reperfusion. Arrow indicates underlying atherosclerotic stenosis. D. Reocclusion and flow stagnation. E. Emergent angioplasty with stenting. F. Final reperfusion. ELVO = emergent large vessel occlusion, IA = intraarterial, ICAS = intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, MCA = middle cerebral artery