FIGURE 8.
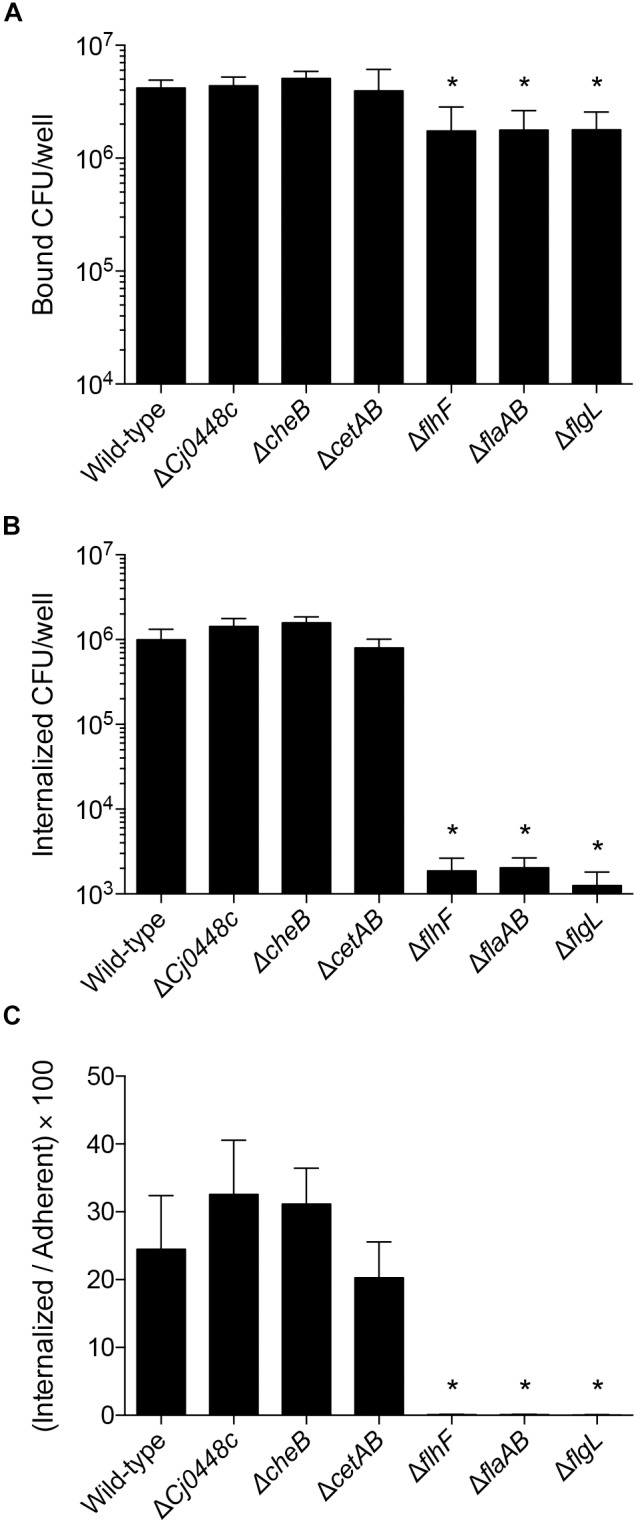
Deletion of chemotaxis genes in C. jejuni does not impair invasion of human INT 407 cells, whereas flagellar regulatory and structural mutants are severely attenuated when compared to the wild-type strain. Human INT 407 cells were infected with C. jejuni for 3 h, and the number of adherent (A) and internalized (B) bacteria were determined using the gentamicin-protection assay. Compared to the wild-type strain, the Cj0448c, cheBR, and cetAB mutants are not deficient in cell adherence or invasion. In fact, the Cj0448c and cheBR show a small but measurable increase in cellular invasion. In contrast, the flhF, flaAB, and flgL flagellar mutants are deficient in cellular adherence and severely impaired in cellular invasion. The number of internalized bacteria divided by the number of adherent bacteria was also calculated (C). Shown is the mean ± the standard deviations. Significant differences from wild-type were determined by a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (∗p < 0.05).
