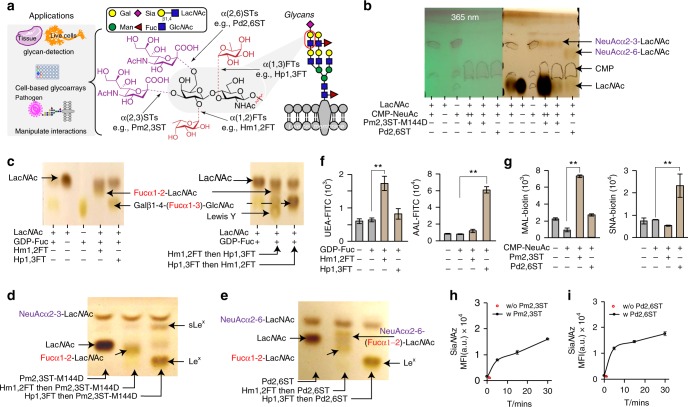
Fig. 1.
Recombinant bacterial FTs and STs for live cell-surface glycan modification. a Specific positions on mammalian cell-surface LacNAc(Galβ1-4-GlcNAc)-containing glycans that can potentially be modified by fucosylation (α1-2- or α1-3-linked) and sialylation (α2-3- or α2-6-linked). Recombinant bacterial glycosyltransferases (FTs and STs) used in this study include Hm1,2FT, Hp1,3FT, Pm2,3ST-M144D, and Pd2,6ST. b Analysis of in vitro sialylation products by TLC. ++ indicates the final reaction system was further mixed with starting material LacNAc, and analyzed by TLC. c Analysis of in vitro fucosylation products by TLC. d, e Analysis of in vitro products generated by a combination of sialylation and fucosylation by TLC. sLeX was formed by combining Hp1,3FT and Pm2,3ST-M144D (d). NeuAcα2-6-(Fucα1-2)-LacNAc was formed by combining Hm1,2FT and Pm2,3ST-M144D (e). f, g Analysis of newly formed glycan epitopes on the cell-surface of Lec2 CHO cells via chemoenzymatic glycan modification. Modified cells were stained by lectins and analyzed by flow cytometry. h, i Evaluation of the substrate tolerance of bacterial sialyltransferases. Unnatural sugar CMP-SiaNAz bearing the azide group were tested for STs. In figures f–i, error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. ** indicated Welch’s t-test P < 0.01. Source data for figures b–i are provided as a Source Data file