Fig. 5.
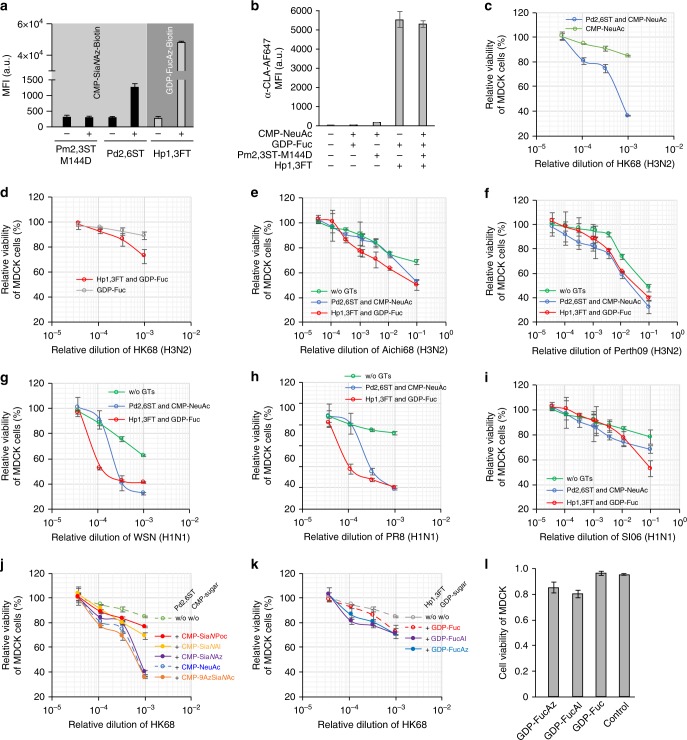
Profiling IAV infection using glycocalyx-modified MDCK cells. a Modification of glycocalyx of MDCK cells using Pm2,3ST-M144D, Pd2,6ST, or Hp1,3ST and the corresponding donor substrate conjugated with biotin. Biotinylated cells were probed with Alexa Fluor 647-Streptavidin. b Modification of glycocalyx of MDCK cells using a combination of Pm2,3ST-M144D and Hp1,3ST. Newly generated sLeX on the MDCK cell surface was confirmed by Alexa Fluor 647-anti-CLA conjugate staining. c Viability of Sia-edited MDCK cells or control cells upon infection by HK68. d Viability of Fuc-edited MDCK cells or control cells infected by HK68. e–i Viability of glycan (Sia or Fuc) edited MDCK cells or control cells upon infection by Aichi68 (e), Perth09 (f), WSN (g), PR8 (h), and SI06 viruses. j–l Viability of glycan edited MDCK cells or control cells upon infection by HK68, using analogs of CMP-Sia (j) or GDP-Fuc (k). Viability of Fuc-edited MDCK cells or control cells, at 10−4 virus dilution (l). In figures a and b, the error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. In c–l, the error bars represent the standard deviation of six biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file