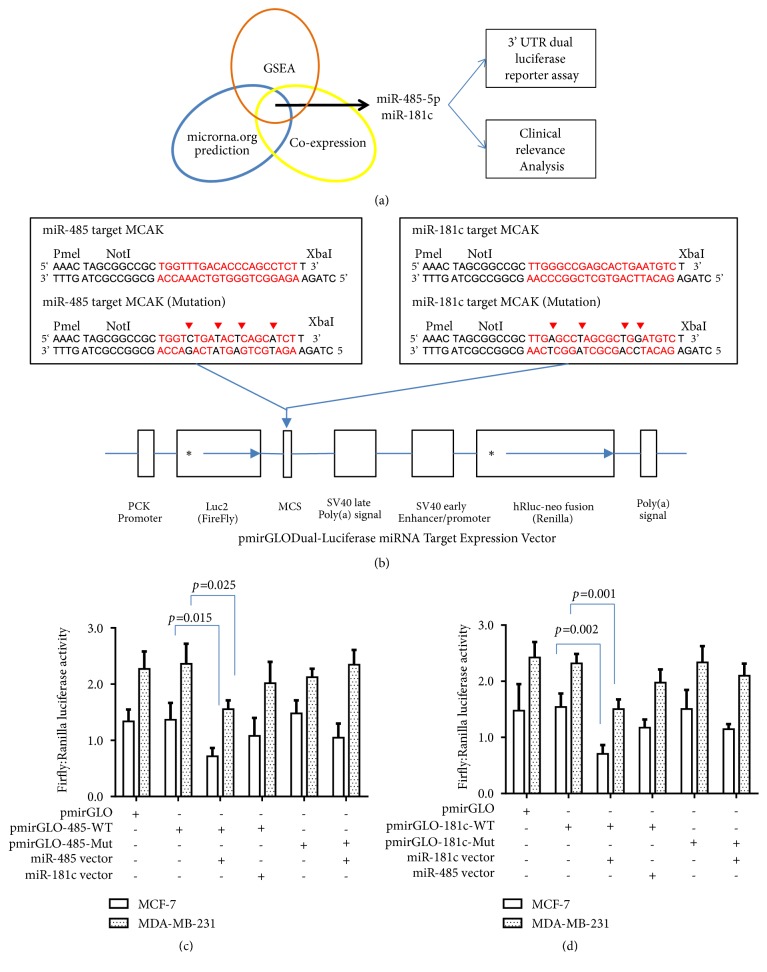
Figure 3.
Identification of microRNAs that modulate expression of MCAK in breast cancer cells. The strategy to identify microRNA modulating MCAK expression was displayed on (a). First, the prediction of target microRNA for MCAK expression was researched on www.microrna.org. Second, the MCAK enriched microRNA gene signatures were also taken into consideration. Meanwhile, those eligible microRNAs were also significantly and negatively correlated with MCAK mRNA levels. Here, miR-485-5p and miR-181 were selected as eligible microRNAs that target MCAK in breast cancer. The double-strand DNA fragments of MCAK binding sites for miR-485-5p and miR-181c were synthesized (b). Mutation fragments were also synthesized for negative control. For each fragment, the PmeI and XhaI restrict enzyme sequence was inserted, and NotI enzyme sequence also inserted for internal control. These fragments were inserted into multiple cloning sites (MCS) of pmirGLO Dual-Luciferase miRNA Target Expression Vector, which was located on 3' untranslated region (3' UTR) of Firefly luciferase (luc2) gene. The pmirGLO-485-5pWT and pmirGLO-181cWT represent wild-type report plasmids of miR-485-5p and miR-181c targeting MCAK, respectively. The pmirGLO-485-5pMut and pmirGLO-181cMut were corresponding to mutants' report plasmids. These report plasmids were transfected into MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells, and luminescence activity was tested after being incubated for 48 hours. The Firefly:Renilla luciferase activity was used to indicate the inhibition rate of reporter systems for miR-485-5p (c) and miR-181c (d), respectively.