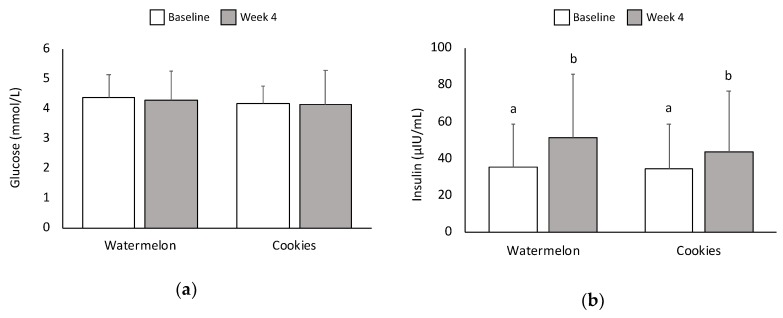
Figure 2.
(a) Effects of WM and LFC on postprandial glucose. No significant differences in blood glucose were observed between snacks and between pre-consumption (pre) and 1-h postconsumption (post). (b) Effects of WM and LFC on postprandial insulin. Blood insulin significantly increased (p < 0.05) in both snacks 1-h postconsumption compared with baseline. Data are presented as means ± SD. Within a variable, values not sharing common superscript are significantly different at p < 0.05.